Are you considering adopting a gluten-free diet? With the increasing popularity of gluten-free products and diets, it’s important to understand the implications and make safe and healthy choices. In this article, we will explore the basics of gluten, the reasons behind choosing a gluten-free diet, potential health benefits, and practical tips for making informed dietary decisions. Whether you have celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, or simply want to explore a gluten-free lifestyle, this article will provide you with the necessary knowledge to make informed choices for your health and well-being.

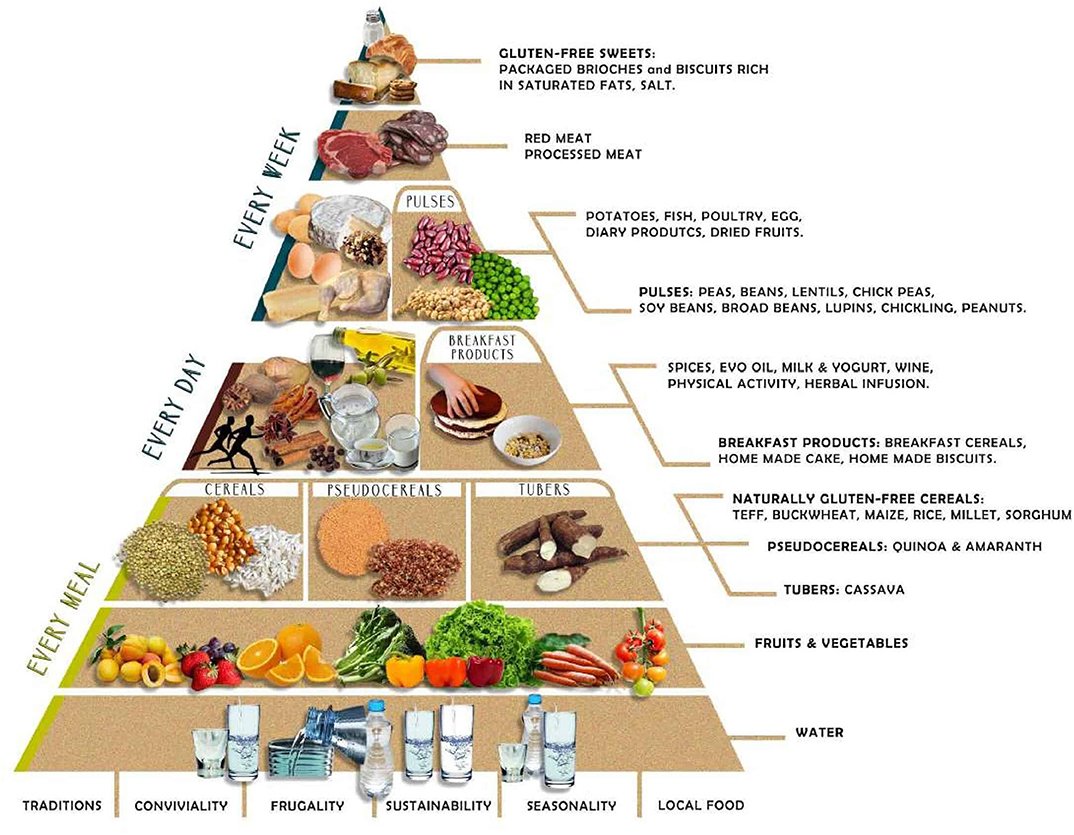
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Understanding Gluten
What is Gluten?
Gluten is a protein composite found in certain grains, such as wheat, barley, and rye. It gives elasticity to dough and helps it hold its shape. Gluten is actually made up of two proteins – gliadin and glutenin. While gluten is harmless for most people, it can cause adverse reactions in individuals with gluten-related disorders.
Gluten-Related Disorders
There are three main gluten-related disorders: celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and wheat allergy. These conditions share some similarities but have distinct characteristics and mechanisms.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten. It affects the small intestine and can lead to damage and inflammation in the lining of the gut. Symptoms vary from person to person but may include digestive issues, fatigue, joint pain, and skin rashes. It is important for individuals with celiac disease to strictly avoid gluten in their diet.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity, also known as gluten intolerance, is a condition where individuals experience symptoms similar to those of celiac disease but without the intestinal damage. The exact mechanisms behind non-celiac gluten sensitivity are still not well understood, but it is believed to involve an immune response to gluten. Symptoms may include bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Wheat Allergy
Wheat allergy is a true allergic reaction to wheat proteins, including gluten. It is an IgE-mediated immune response and can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, difficulty breathing, and even anaphylaxis in severe cases. Unlike celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, wheat allergy specifically involves an allergic response to wheat.
Benefits of Gluten-Free Diets
Improved Digestive Health
One of the primary benefits of a gluten-free diet is improved digestive health, particularly for individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity. By eliminating gluten from their diet, they can alleviate symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Following a gluten-free diet allows the intestinal lining to heal and promotes better overall gut health.
Reduced Inflammation
Gluten has been shown to contribute to inflammation in some individuals, particularly those with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Adopting a gluten-free diet can help reduce systemic inflammation, leading to improved overall health. Lower levels of inflammation have been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Increased Energy Levels
Many individuals report feeling an increase in energy levels after switching to a gluten-free diet. This could be due to reduced digestive discomfort and inflammation. By eliminating gluten, the body can focus its energy on other essential functions, leading to improved vitality and overall well-being.
Better Nutrient Absorption
In individuals with celiac disease, gluten can damage the small intestine, impairing the absorption of essential nutrients. Following a gluten-free diet allows the intestinal lining to heal, improving nutrient absorption and preventing nutrient deficiencies. This is particularly important for vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, and B vitamins.
Weight Loss Potential
While not all gluten-free diets are designed for weight loss, some individuals may experience weight loss as a result of eliminating gluten. This can be attributed to a reduction in calorie intake from processed foods that contain gluten. However, it is important to note that weight loss should not be the primary goal of a gluten-free diet, and maintaining a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is crucial.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Nutritional Deficiencies
One of the main challenges of following a gluten-free diet is the potential for nutritional deficiencies. Gluten-containing grains, such as wheat, are often fortified with essential nutrients like folate and iron. It is important for individuals following a gluten-free diet to ensure they are getting these nutrients from alternative sources, such as fortified gluten-free products or naturally gluten-free foods.
Higher Costs
Gluten-free products can often be more expensive than their gluten-containing counterparts. The production process and the need for specialized ingredients contribute to the higher costs. This can make it more challenging for individuals on a tight budget to maintain a gluten-free diet. It is important to plan meals, shop smartly, and prioritize whole, naturally gluten-free foods to manage costs effectively.
Limited Food Choices
Following a gluten-free diet can also mean limited food choices, especially when dining out or traveling. Many traditional and commonly consumed foods contain gluten, making it necessary to carefully read labels and research restaurant menus. However, with increasing awareness of gluten-related disorders, more gluten-free options are becoming available in stores and restaurants.
Social and Emotional Impact
Adopting a gluten-free diet can have social and emotional implications. It can be challenging to navigate social gatherings, parties, and shared meals where gluten-containing foods are commonly served. Feeling different or isolated from others can also impact one’s emotional well-being. It is essential to communicate openly with friends, family, and support groups to address these challenges.
Hidden Gluten in Foods
Gluten can be found in unexpected food products, making it essential to carefully read food labels and be aware of hidden sources of gluten. Some condiments, sauces, and processed foods may contain gluten as a thickener or filler. Cross-contamination in shared production facilities or kitchens can also lead to the presence of gluten in otherwise gluten-free products. Understanding cross-contamination and seeking certified gluten-free products can help mitigate this risk.
Determining Gluten-Free Status
Reading Food Labels
Reading food labels is crucial when determining the gluten-free status of a product. Look for clear labeling that states “gluten-free” or indicates the absence of gluten-containing grains. Familiarize yourself with common ingredients that may contain gluten, such as wheat, barley, and rye, as well as their derivatives. If in doubt, contacting the manufacturer or referring to trusted gluten-free certification organizations can provide clarity.
Certified Gluten-Free Products
To ensure the gluten-free status of a product, look for certifications from reputable organizations, such as the Gluten-Free Certification Organization (GFCO). These certifications indicate that a product has undergone testing and meets strict standards for gluten-free production. Utilizing certified gluten-free products can provide peace of mind for individuals with gluten-related disorders.
Understanding Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination occurs when gluten-containing and gluten-free products come into contact during production, processing, or preparation. This can happen in shared facilities, equipment, or kitchen environments. Understanding and minimizing the risk of cross-contamination is crucial for individuals who need to follow a strict gluten-free diet. Dedicated gluten-free facilities or separate production lines can help mitigate this risk.
Restaurant Dining
Eating out can pose challenges for individuals on a gluten-free diet. Researching restaurants ahead of time and communicating your dietary needs with the staff can help ensure a safe dining experience. Some restaurants offer gluten-free menus or are knowledgeable about gluten-free options. Asking questions about ingredients, preparation methods, and potential cross-contamination can help make informed choices.
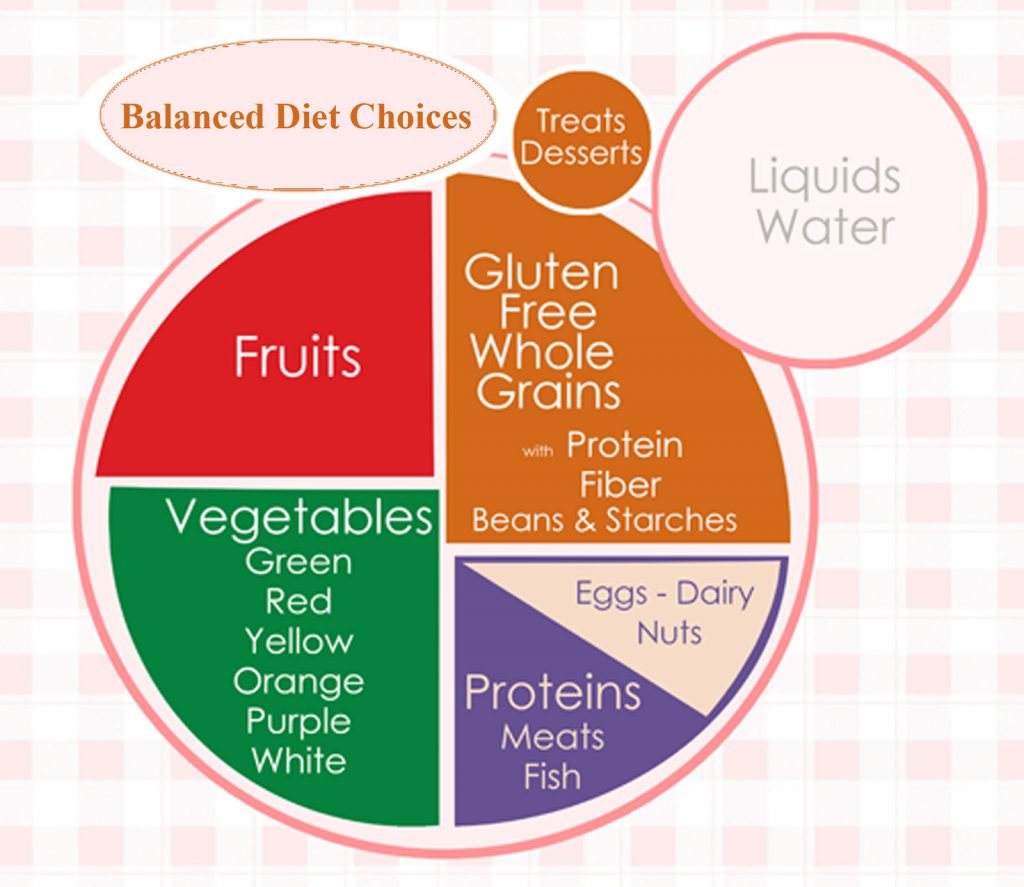
This image is property of glutenfreetrina.com.
Planning a Balanced Gluten-Free Diet
Adequate Macronutrient Intake
When following a gluten-free diet, it is important to prioritize consuming adequate macronutrients, including carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Choose gluten-free sources of carbohydrates such as fruits, vegetables, gluten-free grains, and starchy vegetables like potatoes. Incorporate lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu. Include healthy fats from sources such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.
Incorporating Whole Foods
A balanced gluten-free diet should incorporate a variety of whole, naturally gluten-free foods. These include fruits, vegetables, lean meats, fish, poultry, nuts, seeds, legumes, and gluten-free grains such as quinoa, rice, and corn. These whole foods offer important vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, supporting overall health and well-being.
Choosing Gluten-Free Grains
When selecting gluten-free grains, opt for whole grains to maximize nutritional content and fiber intake. Quinoa, brown rice, amaranth, and buckwheat are excellent gluten-free options that offer a variety of nutrients. However, it is important to ensure that these grains are labeled gluten-free to avoid potential cross-contamination during processing or packaging.
Getting Sufficient Fiber
Adequate fiber intake is important for a healthy digestive system and can be easily achieved on a gluten-free diet. Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, gluten-free grains, legumes, and seeds. If necessary, consider incorporating gluten-free fiber supplements or consulting with a dietitian to ensure you are meeting your daily fiber needs.
Ensuring Vitamin and Mineral Requirements
Eliminating gluten from the diet may inadvertently eliminate certain fortified products, such as breakfast cereals and bread, which provide essential vitamins and minerals. Make sure to choose gluten-free products that are fortified with nutrients, or incorporate alternative sources of these vitamins and minerals into your diet. Consulting with a dietitian can help ensure you meet your specific nutrient requirements on a gluten-free diet.
Gluten-Free Alternatives and Substitutes
Flour Substitutes
Gluten-free flour substitutes are widely available and can be used as alternatives to wheat flour in baking and cooking. Some popular options include rice flour, almond flour, coconut flour, and tapioca flour. Experimenting with different combinations and ratios can help achieve desired textures and flavors in gluten-free recipes.
Bread and Pasta Alternatives
Gluten-free bread and pasta alternatives have come a long way in terms of taste and texture. There are various options available, including bread made from gluten-free grains like rice or quinoa, as well as grain-free bread made from nuts and seeds. For pasta, options such as rice pasta, corn pasta, or pasta made from legumes can be used as substitutes.
Alternative Grains and Seeds
Gluten-free diets can be rich in alternative grains and seeds, offering diverse flavors and textures. Quinoa, amaranth, millet, buckwheat, and teff are excellent gluten-free grains that can be used as side dishes or incorporated into various recipes. Chia seeds, flax seeds, and hemp seeds can be added to smoothies, baked goods, or sprinkled on salads for an extra nutritional boost.
Dairy and Protein Alternatives
Some individuals with gluten-related disorders also have lactose intolerance or prefer to avoid dairy products. Thankfully, there are many dairy alternatives available, such as almond milk, coconut milk, or oat milk. Additionally, for those looking for plant-based protein sources, options like tofu, tempeh, legumes, and quinoa can be incorporated into meals.
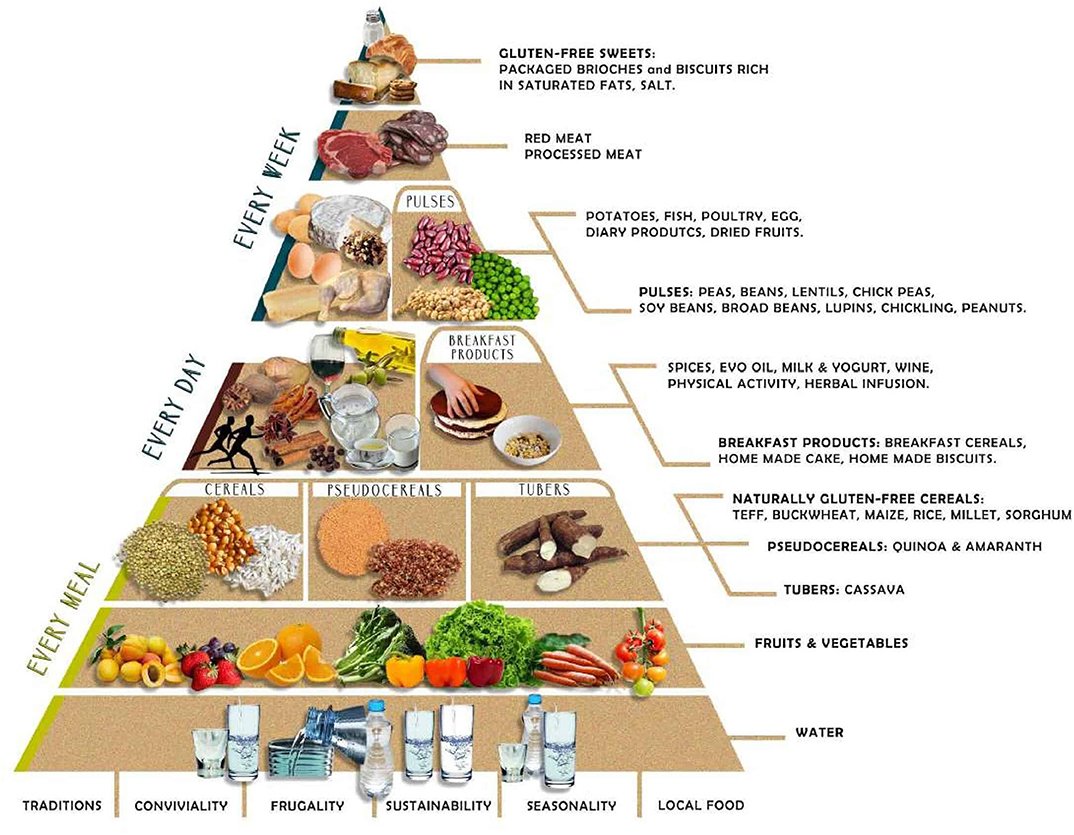
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Meal Prepping Tips
Meal prepping can be a game-changer for individuals on a gluten-free diet. By preparing meals in advance, you can ensure that you always have healthy, gluten-free options readily available. Choose recipes that are naturally gluten-free or can easily be modified, and batch cook for the week. Store individual portions in the refrigerator or freezer for convenience.
Building a Gluten-Free Pantry
Stocking a gluten-free pantry with essential ingredients is essential for successful meal planning. Ensure you have a variety of gluten-free grains, flours, baking ingredients, spices, and condiments on hand. This will allow you to whip up gluten-free meals and snacks without worrying about running out of key ingredients.
Kitchen Utensils and Equipment
Having the right kitchen utensils and equipment can make gluten-free meal preparation easier. Invest in separate cutting boards, cooking utensils, and toasters to avoid cross-contamination. Consider purchasing a dedicated gluten-free toaster or using toaster bags for gluten-free bread. Having a good quality blender and food processor can also help with creating gluten-free alternatives and substitutes.
Recipe Modifications
Adapting recipes to be gluten-free is often necessary when following a gluten-free diet. Familiarize yourself with gluten-free flours and their properties to make appropriate substitutions. Experiment with different recipes and modifications to achieve the desired texture and taste. Online resources, cookbooks, and support groups can be valuable sources of recipe inspiration and guidance.
Eating Out and Traveling on a Gluten-Free Diet
Researching Restaurants
Before dining out, take the time to research restaurants that cater to gluten-free diets. Nowadays, many establishments have gluten-free menus or clearly mark gluten-free options on their regular menus. Check online reviews, consult restaurant websites, or call ahead to confirm their knowledge and accommodation of gluten-free requests.
Communication with Restaurant Staff
When dining out, it is important to effectively communicate your gluten-free needs to restaurant staff. Inform them about your dietary restrictions, ask questions about ingredients and preparation methods, and request proper handling to avoid cross-contamination. Clear communication can help ensure a safe and enjoyable dining experience.
Navigating Travel Challenges
Traveling on a gluten-free diet requires careful planning and preparation. Research gluten-free-friendly destinations and accommodations ahead of time. Pack gluten-free snacks and meals to have on hand during travel. When in doubt, opt for naturally gluten-free foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and nuts. It can also be helpful to bring gluten-free translation cards or apps to communicate your dietary needs in foreign languages.
Packaging Snacks and Meals
Bringing gluten-free snacks and meals with you can help ensure that you always have safe options available. Pack portable snacks such as gluten-free protein bars, nuts, seeds, and dried fruits. For longer trips, consider bringing gluten-free meals or meal kits that can easily be prepared with hot water. Properly packaging these items ensures their freshness and minimizes the risk of cross-contamination.
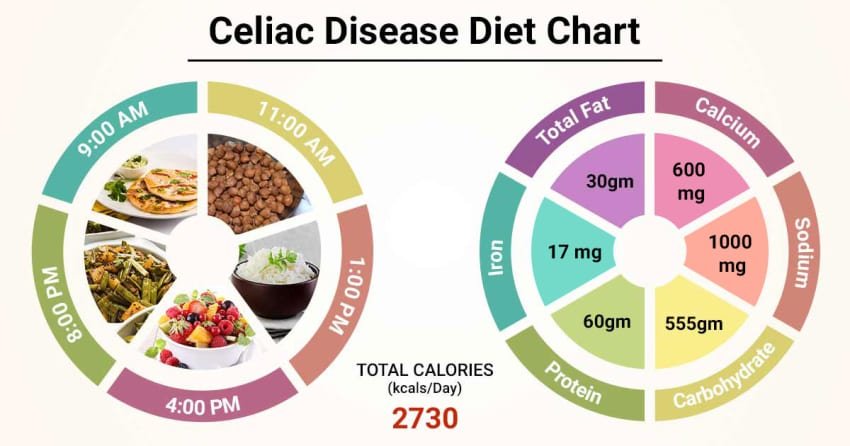
This image is property of assets.lybrate.com.
Addressing Gluten-Free Myths and Misconceptions
Is Gluten-Free Always Healthy?
There is a common misconception that all gluten-free foods are automatically healthy. This is not true, as many gluten-free products can be highly processed and low in nutritional value. It is important to prioritize whole, naturally gluten-free foods and limit intake of processed gluten-free products that are often high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives.
Weight Loss Claims
Another myth surrounding gluten-free diets is that they guarantee weight loss. While some individuals may experience weight loss when adopting a gluten-free diet, it is important to note that this is not the case for everyone. Weight loss should not be the primary goal of a gluten-free diet, and it is crucial to focus on overall health, balanced nutrition, and portion control.
Influence of Media and Fad Diets
The media has popularized gluten-free diets, leading to a surge in popularity and sometimes misinformation. It is important to approach information critically and rely on reputable sources or medical professionals. Avoid falling prey to fad diets that may make unsubstantiated claims about gluten or promote restrictive eating patterns without valid scientific backing.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Consulting with a Dietitian
For individuals with gluten-related disorders or those considering a gluten-free diet, it is advisable to consult with a registered dietitian who specializes in gluten-free nutrition. They can provide personalized guidance and support, ensure nutritional needs are met, and help alleviate any concerns or challenges associated with following a gluten-free diet.
Support Groups and Resources
Joining support groups and accessing resources specific to gluten-related disorders can offer valuable emotional support and practical advice. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of community and help navigate the challenges of a gluten-free lifestyle. Online forums, local support groups, and reputable websites can be useful resources.
Medical Advice for Gluten-Related Disorders
If you suspect you have a gluten-related disorder, it is critical to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis. Consult with your healthcare provider, who may refer you to a gastroenterologist or other specialists for further evaluation. Proper diagnosis is essential to managing these conditions and receiving appropriate medical care.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of gluten, gluten-related disorders, and the potential benefits and challenges of a gluten-free diet is crucial for making informed dietary choices. By arming yourself with the knowledge and resources necessary to navigate gluten-free living, you can achieve a healthy and balanced lifestyle while enjoying delicious, gluten-free meals. Remember to seek professional guidance when necessary, and always prioritize your overall well-being on your gluten-free journey.

This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.