You may have heard about the importance of maintaining a balanced pH in your body, but have you ever wondered if oxalates could have an impact on this delicate equilibrium? Oxalates, naturally occurring compounds found in certain foods, have been a topic of discussion in recent years. In this article, we will explore the potential influence of oxalates on the pH balance in your body. So, get ready to uncover the secrets behind this fascinating connection and gain a deeper understanding of how oxalates could be affecting your overall health.
This image is property of www.labtestsguide.com.
Can Oxalates Influence The pH Balance in The Body?
Oxalates are a type of compound that can be found in certain foods. They have been a topic of debate when it comes to their potential impact on the pH balance in the body. pH balance refers to the level of acidity or alkalinity in our body’s fluids and tissues. It plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and functioning. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between oxalates and pH balance and explore the factors that can affect this delicate equilibrium.
What are Oxalates?
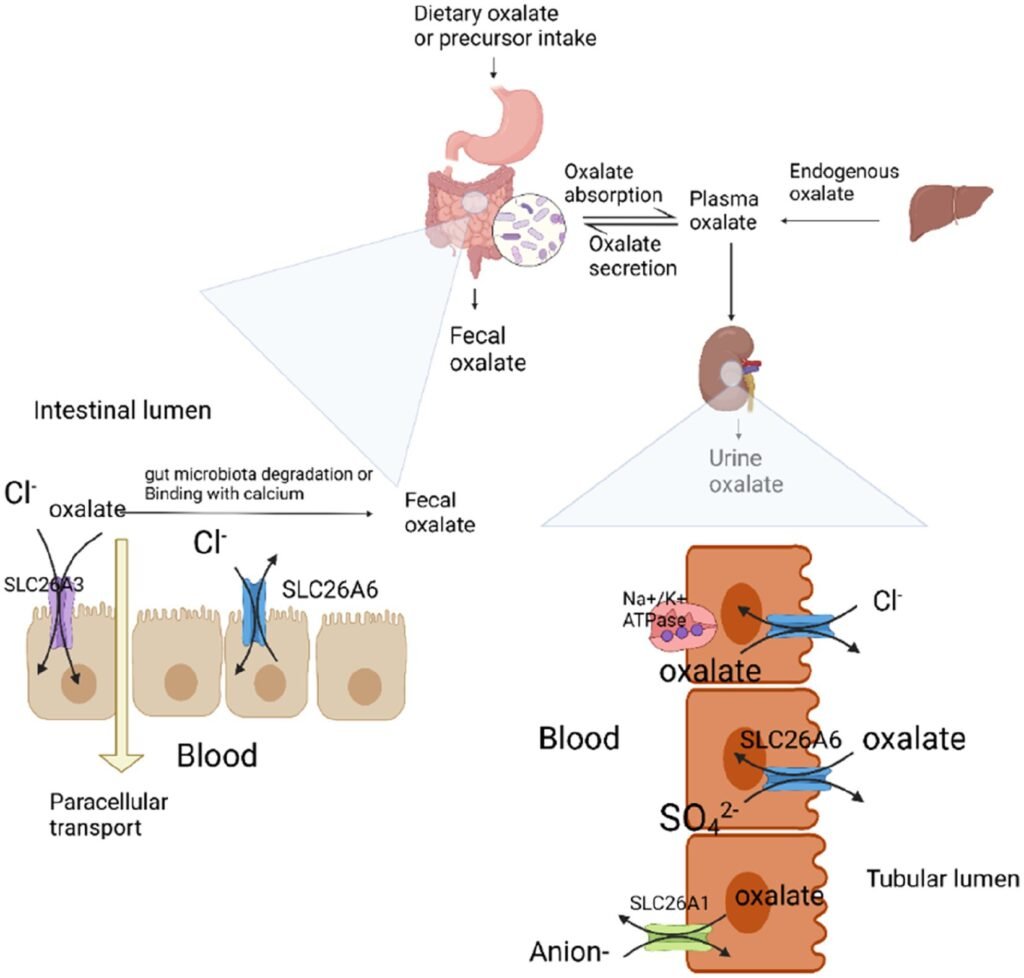
Oxalates, also known as oxalic acid, are naturally occurring compounds found in a variety of plant-based foods. They are classified as antinutrients because they can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals, such as calcium. Oxalates have a unique structure that allows them to bind to minerals, forming insoluble crystals, which can potentially lead to the formation of kidney stones in sensitive individuals.
This image is property of www.frontiersin.org.
Understanding pH Balance
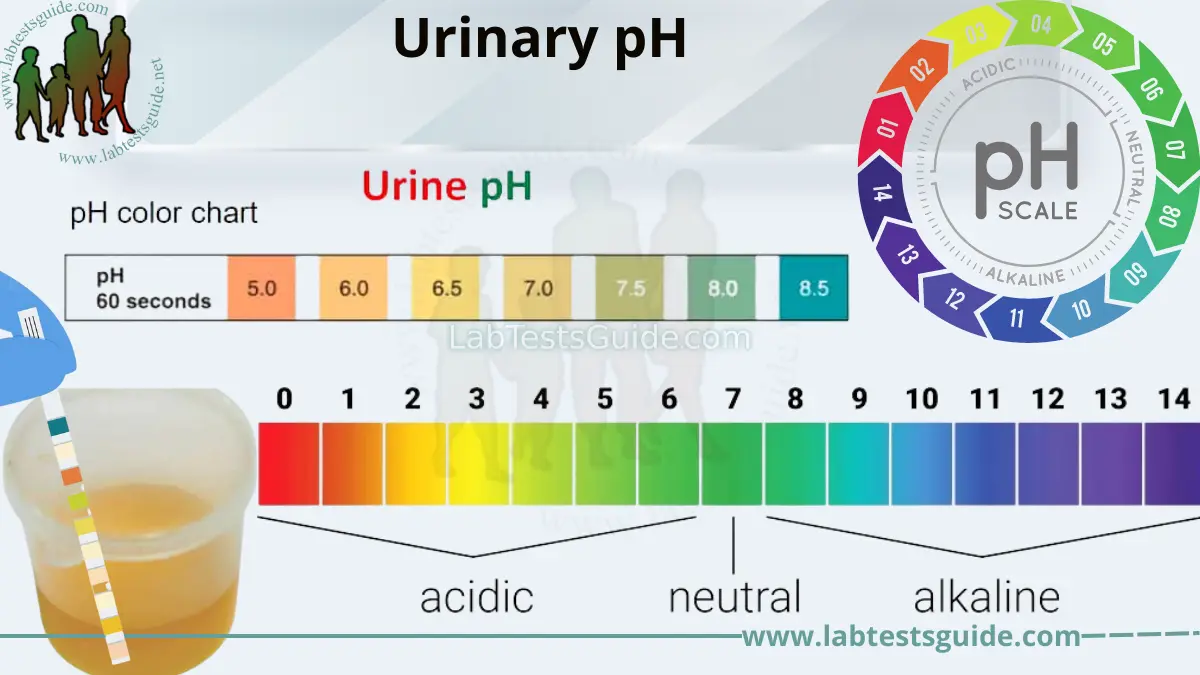
To understand the potential influence of oxalates on pH balance, we first need to understand what pH balance is. pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance, ranging from 0 to 14 on the pH scale. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline. Maintaining the ideal pH balance is crucial for various bodily processes, such as enzyme activity, nutrient absorption, and cellular function.
Oxalates and pH Balance
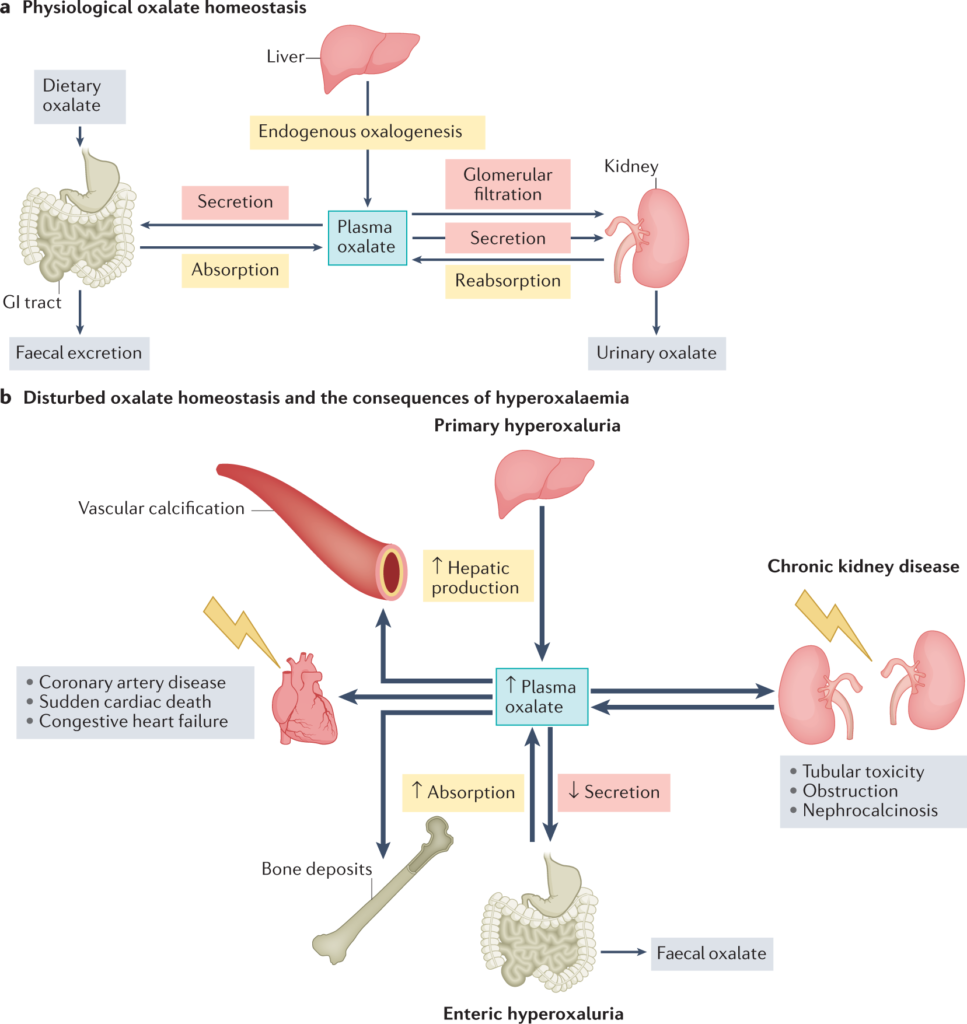
The relationship between oxalates and pH balance is not straightforward. While oxalates themselves do not directly alter the pH of the body, their consumption can indirectly affect the pH balance through various mechanisms. The metabolism of oxalates in the body produces oxalic acid, which is a weak acid. When oxalic acid is present in high concentrations, it can potentially contribute to the acidity of the body fluids.
This image is property of media.springernature.com.
Factors Affecting pH Balance
Several factors can influence the pH balance in our body. These factors include dietary choices, metabolic processes, respiratory function, and renal function.
Dietary Factors:
The foods we consume can have a significant impact on the pH balance in our body. Foods that are rich in acid-forming compounds, such as animal proteins, processed foods, and sugary beverages, can shift the pH towards acidity. On the other hand, foods that are alkaline-forming, such as fruits, vegetables, and certain grains, can help maintain a more alkaline pH.
Metabolic Factors:
Metabolic processes occurring within our body can also affect pH balance. For example, the breakdown of glucose during cellular respiration produces acidic byproducts that need to be efficiently eliminated to maintain pH balance.
Respiratory Factors:
Respiration plays a crucial role in maintaining pH balance by regulating carbon dioxide levels in our body. When we exhale carbon dioxide, it helps to maintain a more alkaline pH. Conditions that affect respiratory function, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can disrupt pH balance.
Renal Factors:
The kidneys play a vital role in regulating pH balance by excreting excess acids or bases through urine. Any impairment in renal function can lead to an accumulation of acidic substances in the body, resulting in an imbalanced pH.
Presence of Oxalates in Foods
Oxalates are found in varying concentrations in a wide range of plant-based foods. Some foods have high oxalate content, while others have moderate or low levels. It is essential to be aware of these distinctions, especially for individuals who are prone to kidney stones or have specific health conditions that may be affected by oxalate consumption.
High Oxalate Foods:
Foods that are particularly high in oxalates include spinach, rhubarb, beet greens, Swiss chard, and certain nuts and seeds, such as almonds and sesame seeds.
Medium Oxalate Foods:
Medium oxalate foods include foods like strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, celery, and green beans. While they contain oxalates, they are not as high as those found in the high oxalate foods.
Low Oxalate Foods:
Foods with low oxalate content include most fruits, such as oranges, apples, and bananas, as well as most vegetables, aside from those mentioned in the high and medium oxalate categories. Grains, legumes, and dairy products also generally have low oxalate levels.
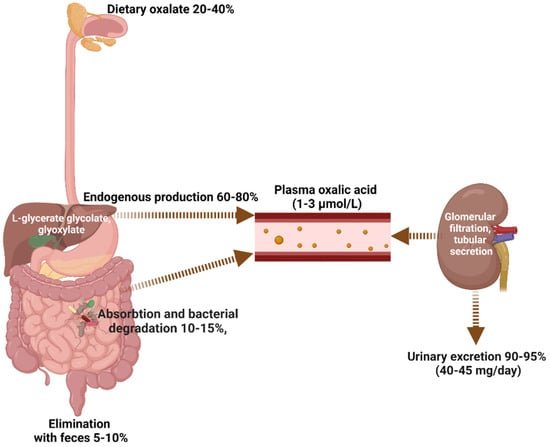
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.
Potential Impact of Oxalates on pH Balance
The consumption of oxalates in food can potentially affect pH balance through various mechanisms. Oxalates contribute to the production of oxalic acid during metabolism, which can increase acidity in the body. Additionally, oxalic acid can bind with minerals like calcium, interfering with their absorption and potentially affecting the pH balance.
Effects of Acidic pH on the Body
Maintaining a balanced pH is crucial for overall health. When the pH balance becomes too acidic, it can lead to a condition known as acidosis. Acidosis can have various negative effects on the body, such as decreased enzyme activity, impaired immune function, reduced muscle performance, and increased risk of certain diseases, including osteoporosis and kidney stones.
This image is property of pub.mdpi-res.com.
Role of Oxalates in Acidic pH
While oxalates themselves do not directly cause acidosis, their metabolism can contribute to an acidic environment in the body. When oxalic acid is present in high concentrations, it can promote acidity and potentially disrupt pH balance. This acidic environment can increase the risk of conditions like kidney stone formation, as well as other health issues associated with acidosis.
Alkaline Diets and pH Balance
Some individuals opt for alkaline diets in an attempt to maintain a more alkaline pH in their body. These diets typically involve consuming larger quantities of alkaline-forming foods and reducing or avoiding acidic foods. While alkaline diets have gained popularity, it is essential to note that the body has its mechanisms to regulate pH balance, and the impact of diet on overall pH is often limited.
Managing pH Balance with Oxalate-rich Foods
For individuals who are concerned about the potential impact of oxalates on pH balance, there are strategies to manage oxalate intake while still enjoying a diverse and nutritious diet. Cooking or steaming high oxalate foods can help reduce their oxalate content. Additionally, consuming calcium-rich foods alongside oxalate-rich foods can help bind with oxalates and reduce their absorption.
Conclusion
While oxalates can potentially influence the pH balance in the body, their impact is indirect and can vary depending on numerous factors. Maintaining a balanced pH is essential for overall health, and a variety of factors, including diet, can affect this delicate equilibrium. Understanding the presence of oxalates in foods and making informed dietary choices can help individuals manage their oxalate intake while still maintaining optimal pH balance. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for individualized guidance on maintaining pH balance and managing oxalate consumption.