So you’re enjoying a refreshing glass of your favorite beverage, but have you ever stopped to consider what exactly is in it? Well, one element that may surprise you is oxalate. Yes, the infamous oxalate, known for its association with kidney stones, can actually be found lurking in your favorite drinks. But before you panic and give up on all beverages forever, let’s take a closer look at what this means, how it can affect you, and which drinks to watch out for. So grab your drink and let’s dive into the world of oxalate in beverages.

This image is property of www.thekidneydietitian.org.
Types of Oxalates
When it comes to oxalates, there are various types that can be found in beverages. The most common types of oxalates found in drinks include calcium oxalate, sodium oxalate, and potassium oxalate. These oxalates can have different effects on our health, particularly when consumed in excessive amounts. In the following sections, we will explore the impact of oxalates on our health and the different levels of oxalates in common beverages.

This image is property of www.thekidneydietitian.org.
Impact of Oxalate on Health
Kidney Stone Formation
One of the most well-known impacts of oxalates on health is their association with kidney stone formation. Oxalates can combine with calcium in the urine, forming crystals that can lead to the development of kidney stones. This can be especially problematic for individuals who are prone to forming kidney stones or already have a history of kidney stone issues.
Calcium Absorption Interference
Consuming high levels of oxalates can also interfere with calcium absorption in the body. Oxalates have the ability to bind with calcium, forming insoluble calcium oxalate crystals that cannot be easily absorbed by the intestines. This can potentially lead to calcium deficiency and impact bone health in the long run.
Urinary Tract Infections
Some studies suggest that high levels of oxalates in beverages may also contribute to the development of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Oxalates can irritate the urinary tract and promote the growth of bacteria, increasing the risk of UTIs. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between oxalates and UTIs.

This image is property of sallyknorton.com.
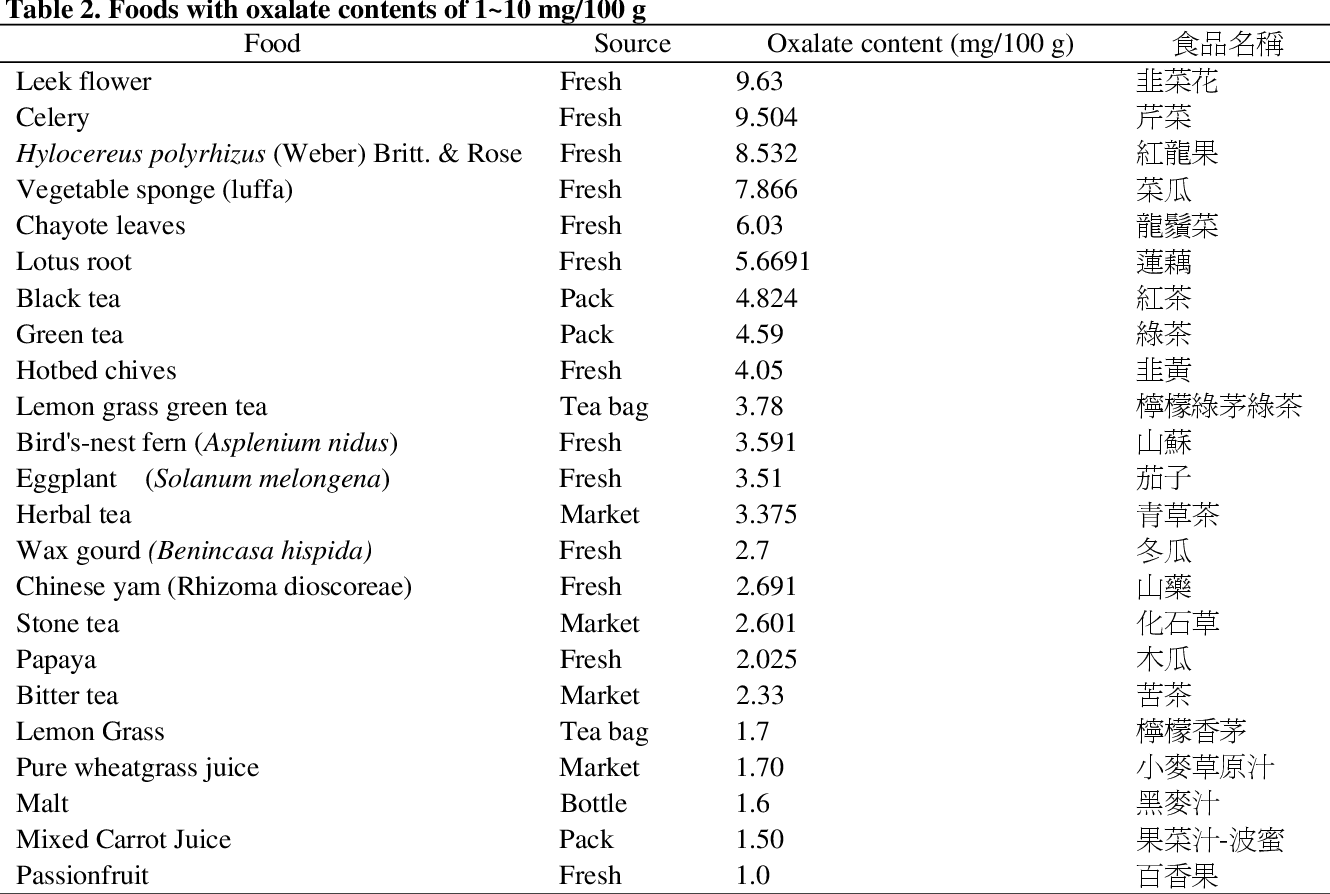
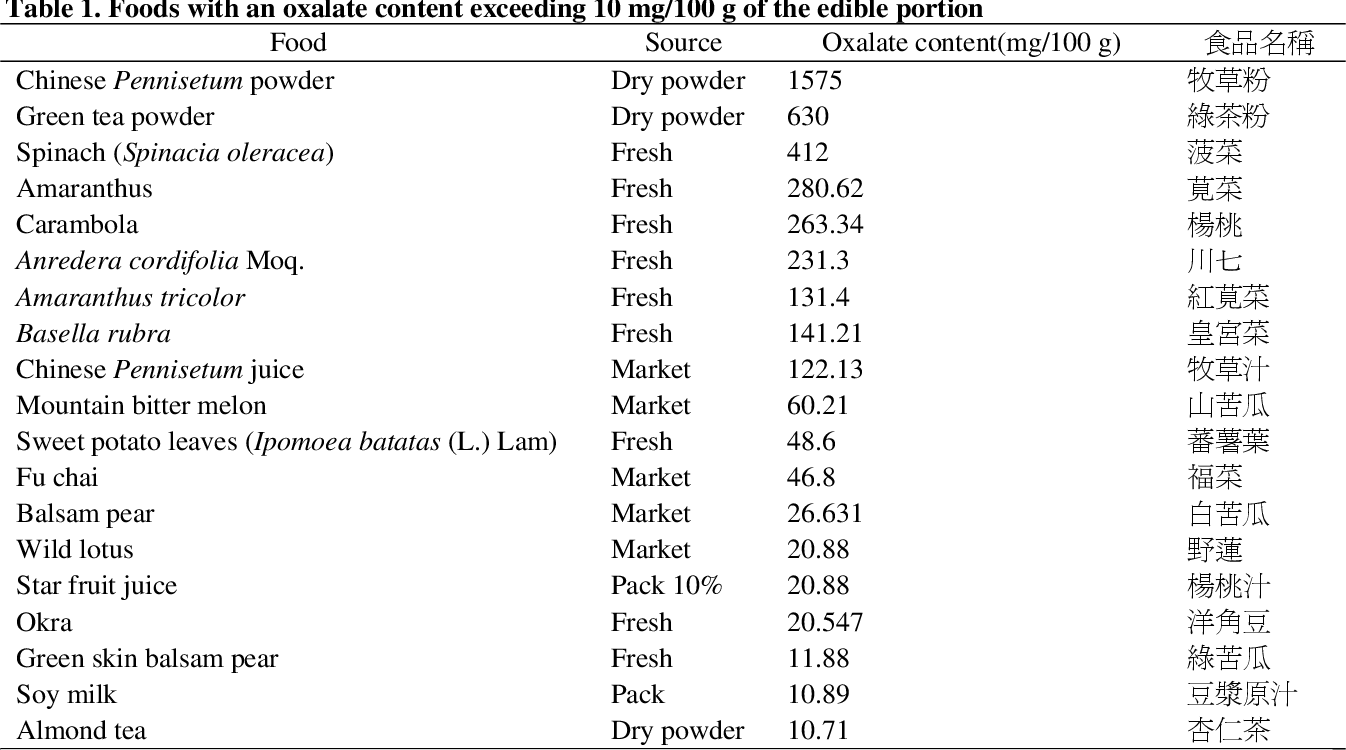
Common Beverages Containing Oxalate
To better understand the levels of oxalates in different beverages, let’s take a look at some popular drinks that can contain significant amounts of oxalates.
Tea
Tea is a beloved beverage consumed by millions around the world. While it offers numerous health benefits, it is important to be mindful of its oxalate content. Tea, especially black tea and green tea, can contain moderate to high levels of oxalates. However, herbal teas generally have lower oxalate levels compared to black or green tea.
Coffee
Coffee is a staple for many individuals, providing a morning pick-me-up or a midday energy boost. However, just like tea, coffee can also contribute to oxalate intake. Instant coffee, brewed coffee, and decaffeinated coffee all contain varying levels of oxalates. It is worth noting that decaffeinated coffee typically has higher oxalate levels compared to regular coffee.
Beer
Enjoying a cold beer on a hot day is a common way to unwind and relax. While beer may not be the first beverage that comes to mind when thinking about oxalates, certain types of beer can indeed contain them. Lager, ale, and stout are the main beer variants that may have measurable oxalate content.
Wine
Wine is a popular choice for those looking to unwind or pair a drink with their meal. Both red wine and white wine can contain oxalates, although the levels may differ. Red wine is often considered to have higher oxalate levels compared to white wine. Rosé wine, made from a blend of red and white varieties, may also contain oxalates but in varying amounts.
Soft Drinks
Soft drinks provide a refreshing and bubbly treat on various occasions. However, it’s important to be aware that certain soft drinks can contribute to oxalate intake. Cola, lemon-lime, orange, and root beer are some common types of soft drinks that may contain oxalates.
This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Oxalate Levels in Different Beverages
To understand the impact of oxalates in specific beverages, it’s helpful to know the approximate levels found in each. Here is a breakdown of the oxalate levels in some popular beverages:
Tea
- Black Tea: 4-8 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Green Tea: 2-7 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Herbal Tea: Varies, but generally lower oxalate levels compared to black or green tea
Coffee
- Instant Coffee: 1-2 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Brewed Coffee: 2-4 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Decaffeinated Coffee: Higher oxalate levels compared to regular coffee, but exact amounts may vary
Beer
- Lager: Varies, but generally low amounts of oxalates
- Ale: Varies, but generally low to moderate amounts of oxalates
- Stout: Varies, but may have moderate to high oxalate levels
Wine
- Red Wine: 2-3 mg of oxalates per 150 ml (5 oz) serving
- White Wine: 1-2 mg of oxalates per 150 ml (5 oz) serving
- Rosé Wine: Varies, but generally levels similar to red or white wine
Soft Drinks
- Cola: 2-4 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Lemon-Lime: 0-1 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Orange: 0-1 mg of oxalates per 240 ml (8 oz) serving
- Root Beer: Varies, but generally low amounts of oxalates
This image is property of d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net.
Reducing Oxalate Levels in Beverages
If you are concerned about the oxalate levels in your favorite beverages, there are some methods you can try to help reduce the oxalate content:
Blanching
Blanching involves briefly immersing fruits or vegetables in boiling water followed by rapid cooling. This technique can help reduce the oxalate levels in certain produce.
Boiling
Boiling vegetables or fruits can also help lower their oxalate content. However, it’s important to note that boiling may cause water-soluble nutrients to leach out as well.
Steaming
Steaming is another cooking method that can help reduce oxalate levels in vegetables. Steaming preserves more nutrients compared to boiling, making it a preferred method for many individuals.
Soaking
Soaking certain foods, such as legumes, can help reduce oxalate levels. Discarding the soaking water before cooking can further decrease oxalate content.
Fermenting
Fermentation is a traditional method that can lower oxalate levels in some foods. Fermented beverages, such as kombucha, may have decreased oxalate content compared to their non-fermented counterparts.
In conclusion, oxalates can be found in various beverages, and their impact on health varies. While oxalates can contribute to kidney stone formation, interfere with calcium absorption, and potentially increase the risk of urinary tract infections, it’s important to remember that moderate consumption of beverages containing oxalates is unlikely to cause significant health issues. By being mindful of your oxalate intake and exploring methods to reduce oxalate levels in beverages, you can still enjoy your favorite drinks while taking care of your overall well-being.

