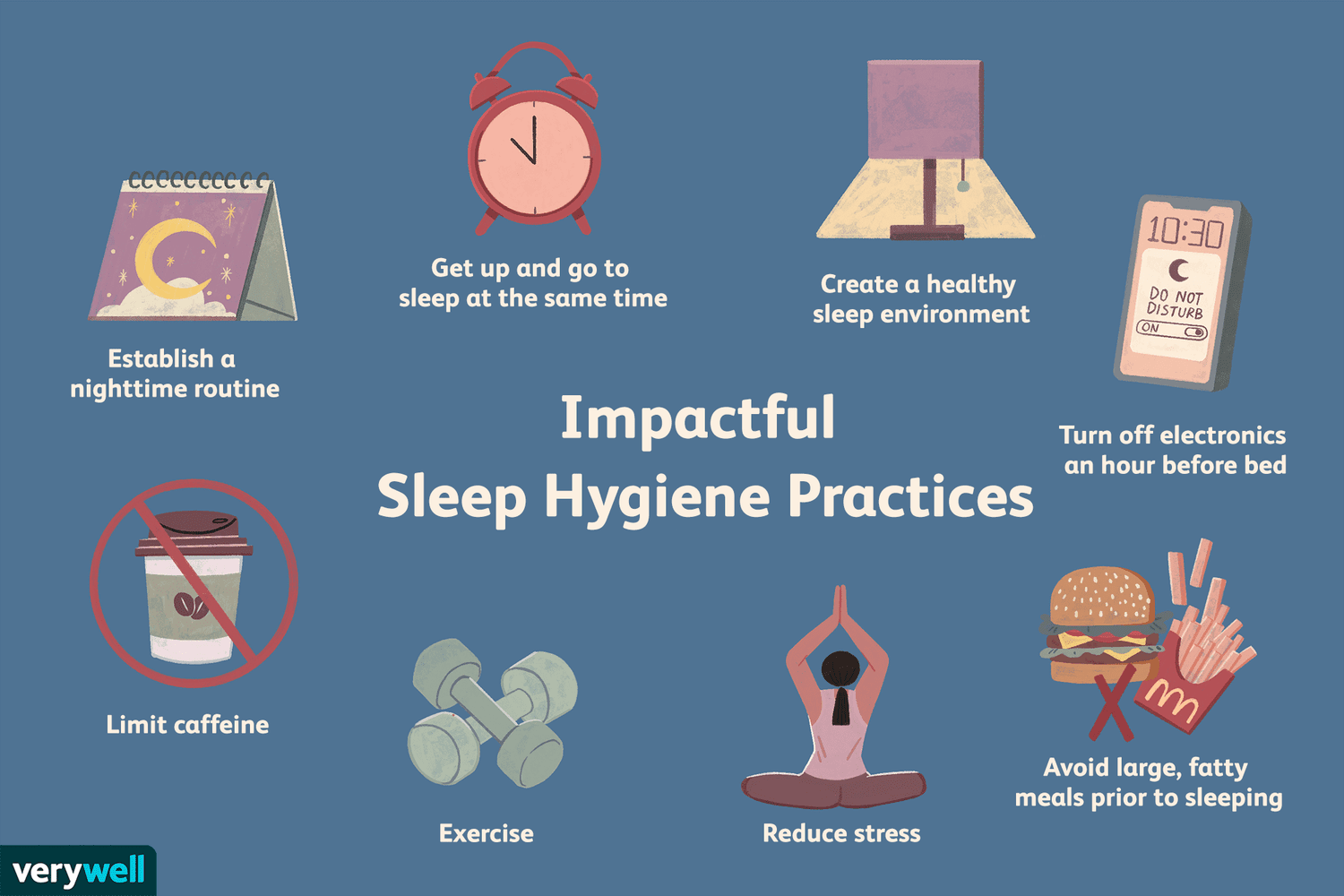
Are you struggling to get a good night’s sleep? Look no further! This article will explore the fascinating connection between nutrition and sleep, and how making some simple changes to your diet can greatly improve your rest and overall well-being. We’ll dive into the science behind it all, discuss the foods that promote better sleep, and provide practical tips to help you incorporate these changes into your daily routine. So, get ready to discover the secret to achieving a peaceful and rejuvenating slumber.
Importance of Nutrition for Sleep
How Diet Affects Sleep Quality
Having a healthy and balanced diet plays a crucial role in getting a good night’s sleep. The food we consume throughout the day provides our bodies with the necessary nutrients to support various bodily functions, including sleep. Certain dietary habits and choices can either enhance or hinder the quality of our sleep.
The Role of Macronutrients in Sleep
Macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, all have a significant impact on sleep quality. Carbohydrates help increase the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and improves sleep. Protein-rich foods contain tryptophan, an amino acid that aids in the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Consuming healthy fats, like those found in avocados or nuts, can help keep you fuller for longer and promote a more restful sleep.
The Impact of Micronutrient Deficiencies on Sleep
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, also play a vital role in sleep regulation. Deficiencies in certain micronutrients can lead to sleep disturbances. For example, magnesium deficiency has been linked to insomnia and poor sleep quality. Adequate levels of calcium are necessary for the body to produce melatonin, which is essential for maintaining a healthy sleep pattern. Vitamin D deficiency has also been associated with sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea.
Food and Beverages to Promote Better Sleep
Incorporating specific foods and beverages into your diet can greatly enhance your sleep quality. Foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey, salmon, and nuts, can help promote better sleep. Additionally, consuming foods high in melatonin, such as tart cherries or kiwis, can have a positive impact on sleep. Herbal teas, like chamomile or valerian root, are also known for their calming properties and can improve sleep quality.
Sleep and Dietary Patterns
Effects of Different Diets on Sleep
The type of diet you follow can significantly affect your sleep quality. For example, a diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to poor sleep patterns. On the other hand, a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support optimal sleep.
Optimal Eating Patterns for Quality Sleep
In addition to the specific types of food consumed, eating patterns also play a role in sleep quality. It is generally recommended to have regular meal times and avoid heavy meals close to bedtime. Eating a balanced dinner with a variety of nutrients can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent disruptions during sleep.
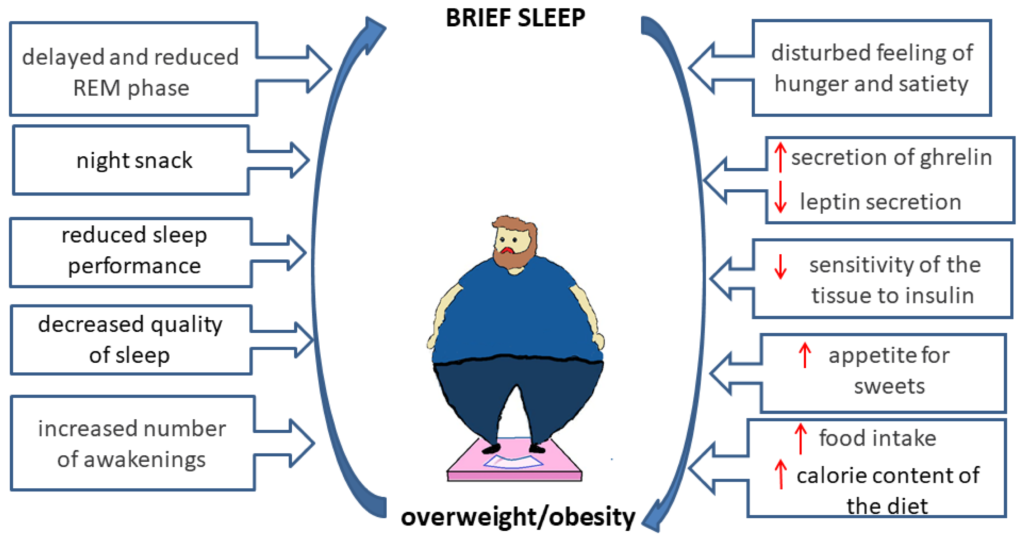
Effects of Late-Night Eating on Sleep
Eating late at night, especially heavy or high-calorie meals, can negatively impact sleep quality. Digestion requires energy, and consuming large meals before bed can make it harder for the body to fully relax and enter into a deep sleep. It is best to have your last meal at least a few hours before bedtime to allow for proper digestion.
Intermittent Fasting and Sleep Quality
Intermittent fasting, a popular eating pattern that involves regular fasting periods, has gained attention for its potential benefits on various aspects of health. Some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help improve sleep quality. However, it is important to note that individual experiences may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended before starting any fasting regimen.
This image is property of cds.cern.ch.
Sleep-Inducing Foods
Foods that Naturally Promote Sleep
Certain foods are known for their sleep-inducing properties and can help you fall asleep faster and have a more restful sleep. Examples include bananas, which are rich in magnesium and potassium, and are known to promote muscle relaxation. Additionally, oats contain melatonin, which can help regulate sleep patterns.
Incorporating Foods Rich in Tryptophan
Tryptophan-rich foods are beneficial for sleep as the body converts tryptophan into serotonin and melatonin, hormones that promote sleepiness. Foods such as turkey, chicken, tofu, nuts, and seeds are all good sources of tryptophan. Incorporating these foods into your diet can contribute to better sleep quality.
The Benefits of Melatonin-Rich Foods
Melatonin is a hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycles. Consuming foods that naturally contain melatonin can be an effective way to improve sleep. Tart cherries, specifically Montmorency cherries, have been found to be particularly high in melatonin. Drinking tart cherry juice or consuming the fruit itself can have a positive impact on sleep quality.
Herbal Teas to Enhance Sleep Quality
Herbal teas have long been used as natural remedies for promoting relaxation and improving sleep. Chamomile tea is one of the most well-known and widely consumed herbal teas known for its calming properties. Other herbal teas such as valerian root, lavender, and passionflower can also help relax the mind and body, preparing you for a good night’s sleep.
Avoiding Sleep-Disrupting Foods
Foods that Negatively Impact Sleep
Just as certain foods can promote sleep, others can have a negative impact on sleep quality. Foods high in refined sugars, such as sugary snacks or desserts, can lead to energy spikes and crashes, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Spicy foods and those high in saturated or trans fats can also contribute to indigestion and discomfort, which can interfere with sleep.
Effects of Caffeine and Alcohol on Sleep
Caffeine and alcohol, two popular beverages, can significantly affect sleep patterns. Consuming caffeinated beverages, such as coffee or energy drinks, too close to bedtime can interfere with falling asleep. Alcohol, although it may initially make you feel drowsy, can disrupt the quality of your sleep and lead to frequent awakenings throughout the night.
Spicy and Acidic Foods and Sleep Disturbances
Spicy foods or those high in acidity can cause discomfort and heartburn, especially when consumed close to bedtime. This discomfort can make it challenging to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. Avoiding these types of foods, especially in the evening, can help promote better sleep quality.
The Impact of Late-Night Snacking on Sleep
Late-night snacking, particularly on unhealthy and calorie-dense foods, can lead to weight gain and poor sleep quality. Consuming large amounts of food before bed can disrupt digestion and increase the chance of acid reflux or heartburn. It is recommended to limit late-night snacking and prioritize healthier options if necessary.

This image is property of iamherbalifenutrition.com.
Nutrients Essential for Restful Sleep
Magnesium and Its Role in Sleep Regulation
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in sleep regulation. It is involved in the production of GABA, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleep. Consuming magnesium-rich foods, such as leafy green vegetables, legumes, and nuts, can help support restful sleep.
The Influence of Calcium on Sleep Quality
Calcium is not only essential for bone health but also for proper sleep-wake regulation. Adequate calcium levels are necessary for the production of melatonin, the hormone that signals the body to prepare for sleep. Incorporating calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk can support better sleep quality.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Sleep Disorders
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to various health issues, including sleep disorders. Research suggests that low vitamin D levels may increase the risk of sleep disturbances, such as insomnia and sleep apnea. To maintain optimal vitamin D levels, it is important to spend time in the sun, incorporate fatty fish into your diet, or consider taking a vitamin D supplement as advised by a healthcare professional.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Better Sleep
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including improving sleep quality. These essential fats support brain health and reduce inflammation, promoting better overall sleep. Including omega-3-rich foods or considering a fish oil supplement can be beneficial for your sleep hygiene.
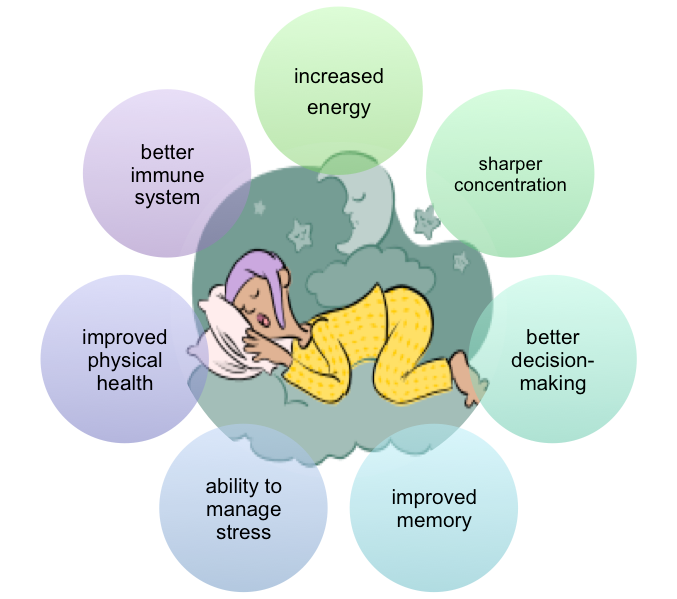
Optimizing Sleep Hygiene through Nutrition
Balancing Meals to Improve Sleep
Eating balanced meals that include a combination of macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote better sleep. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals can contribute to improved sleep hygiene.
Eating Timing and Its Effects on Sleep
The timing of your meals can also impact sleep quality. Consuming large meals or heavy snacks too close to bedtime can interrupt digestion and lead to discomfort, making it hard to fall asleep. It is generally recommended to eat your last meal at least a few hours before bed to allow for proper digestion.
The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity has numerous benefits for overall health, including sleep quality. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or jogging, can help regulate sleep-wake cycles and improve sleep duration and quality. It is important to note that intense exercise close to bedtime may have a stimulating effect and make it harder to fall asleep, so timing your workouts earlier in the day is recommended.
Hydration and Its Impact on Sleep Quality
Staying adequately hydrated throughout the day can positively impact sleep quality. Dehydration can lead to discomfort and can contribute to sleep disturbances. It is recommended to drink enough water or other hydrating beverages throughout the day, while also being mindful of not consuming excessive fluids close to bedtime to avoid disruptions from bathroom trips.
This image is property of www.mankatoclinic.com.
The Gut-Brain Connection and Sleep
How Gut Health Affects Sleep
The gut-brain connection plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including sleep. An imbalance in gut health, such as an overgrowth of harmful bacteria or a lack of beneficial bacteria, can lead to sleep disturbances. Taking care of your gut health by consuming a balanced diet that includes fiber-rich foods and incorporating probiotics can positively impact sleep.
The Role of Gut Microbiota in Sleep Regulation
The gut microbiota refers to the community of microorganisms that reside in the gastrointestinal tract. Emerging research suggests that these microorganisms can influence sleep regulation. Some strains of bacteria found in the gut produce neurotransmitters that affect sleep quality and can influence melatonin production. Consuming probiotic-rich foods or taking a probiotic supplement can help support a healthy balance of gut microbiota.
Probiotics and Their Effects on Sleep
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can promote a healthy gut environment. Studies have shown that certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can positively influence sleep quality. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet can help support a healthy gut and improve sleep.
The Impact of Prebiotics on Sleep Patterns
Prebiotics are a type of fiber that serves as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Consuming prebiotic-rich foods can help nourish the gut microbiota. While research on prebiotics specifically related to sleep is limited, maintaining a diverse and healthy gut microbiota through the consumption of fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains may indirectly support better sleep patterns.
Meal Planning for Better Sleep
Creating Well-Balanced Sleep-Friendly Meals
Meal planning can play a significant role in optimizing sleep quality. Creating well-balanced meals that include a variety of nutrients can provide the necessary components for optimal sleep. Incorporating lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats into your meals can support better sleep and overall well-being.
Snack Ideas for a Good Night’s Sleep
Choosing the right snacks before bed can help promote a good night’s sleep. Opt for snacks that contain a combination of carbohydrates and protein, such as a small bowl of whole-grain cereal with milk or a piece of whole-grain toast with almond butter. These snacks provide a steady release of energy and ensure that you won’t go to bed hungry.
Meal Prepping to Support Optimal Sleep
Meal prepping can be a helpful strategy to ensure that you have nutritious meals readily available, even during busy times. By preparing your meals in advance, you can prioritize sleep and avoid relying on less healthy food options when time is limited. Consider batch cooking and portioning out meals for the week to make sleep-friendly eating more convenient.
Recipes Incorporating Sleep-Boosting Ingredients
Incorporating sleep-boosting ingredients into your recipes can be an enjoyable way to support better sleep. For example, you can try making a spinach and feta omelet with a side of whole-grain toast for breakfast, followed by a grilled salmon with quinoa and roasted vegetables for dinner. Experimenting with recipes that include sleep-friendly ingredients can bring variety and enhance your overall sleep hygiene.

This image is property of www.verywellmind.com.
Eating Disorders and Sleep Disturbances
Anorexia Nervosa and Its Effects on Sleep
Anorexia nervosa, an eating disorder characterized by extreme weight loss, can lead to severe sleep disturbances. Insomnia, frequent awakenings, and daytime sleepiness are common sleep issues experienced by individuals with anorexia nervosa. Proper treatment for the eating disorder, coupled with a focus on restoring a healthy and balanced diet, is essential for addressing sleep disruptions.
Bulimia Nervosa and Sleep Quality
Bulimia nervosa, an eating disorder characterized by binge-eating followed by compensatory behaviors, can also have negative effects on sleep quality. The physical and emotional stress associated with the disorder can lead to sleep disruptions, including insomnia and restless sleep. Seeking professional help and engaging in treatment for bulimia nervosa can help improve sleep patterns.
The Relationship between Binge Eating and Insomnia
Binge eating disorder and other forms of compulsive overeating can negatively impact sleep. Late-night binge eating can lead to discomfort, indigestion, and difficulty falling asleep. Addressing the underlying causes of binge eating through therapy and adopting healthier coping mechanisms may contribute to improved sleep quality.
Night Eating Syndrome and Disrupted Sleep
Night eating syndrome is a condition characterized by consuming a significant portion of daily calories during nocturnal hours. It can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, with individuals waking up multiple times during the night to eat. Therapy and behavioral interventions aimed at addressing night eating syndrome can help restore healthy eating and sleep patterns.
Professional Advice and Expert Recommendations
Consulting with a Registered Dietitian
When it comes to optimizing nutrition for sleep, consulting with a registered dietitian can provide valuable guidance and personalized recommendations. A registered dietitian can assess your specific nutritional needs, help identify any deficiencies, and create a tailored meal plan to support optimal sleep. They can also provide guidance on specific dietary concerns related to sleep disorders or eating disorders.
Sleep Specialists and Dietary Recommendations
Sleep specialists, such as sleep physicians or psychologists specializing in sleep disorders, can provide insights into the connection between nutrition and sleep. They can offer specific dietary recommendations based on your sleep disorder or specific sleep-related concerns. Working in collaboration with sleep specialists can help optimize your overall sleep quality.
Integrating Nutrition and Sleep Therapy
In some cases, integrating nutrition interventions with sleep therapy may be beneficial. For individuals with sleep disorders or chronic insomnia, combining behavioral techniques, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), with dietary adjustments can provide comprehensive support for sleep improvement. This integrated approach can address both behavioral and physiological factors contributing to sleep disturbances.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Improving Rest
To improve rest and well-being through nutrition and sleep, it is crucial to rely on evidence-based strategies. Every individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Keeping up-to-date with the latest research and consulting with healthcare professionals can ensure that you are making informed decisions about your diet and sleep hygiene. Prioritizing evidence-based strategies can help you optimize your rest and overall well-being.
In conclusion, nutrition and sleep are interconnected, and what you eat can significantly impact the quality of your sleep. By focusing on a well-balanced diet that includes macronutrients and micronutrients essential for sleep regulation, and avoiding sleep-disrupting foods, you can enhance your sleep quality. Additionally, incorporating sleep-inducing foods and practicing good sleep hygiene, such as balancing meals, eating timing, regular physical activity, and staying hydrated, can further optimize your rest. Consider the gut-brain connection, meal planning, and professional advice to address specific sleep-related concerns or conditions. Remember, it’s essential to prioritize evidence-based strategies and consult with healthcare professionals to tailor your nutrition and sleep approaches for improved rest and overall well-being.
This image is property of www.mdpi.com.