So you’ve been diagnosed with kidney stones, and you’re eager to prevent them from recurring. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll be discussing the crucial role of medication management in kidney stone prevention. From understanding the types of medications available to learning how to effectively incorporate them into your daily routine, we’ll provide you with the necessary knowledge and strategies to keep those pesky stones at bay. So let’s dive into the world of medication management and take control of your kidney stone prevention journey.
Medication Management In Kidney Stone Prevention
Kidney stones can be an extremely painful and debilitating condition. They are formed when certain substances in the urine, such as calcium and oxalate, become concentrated and crystallize to form stones. These stones can range in size from tiny grains to larger, more obstructive masses. Fortunately, there are various medications available that can help in the prevention of kidney stones, reducing the risk of recurrence and the potential for further complications. Let’s explore the different types of kidney stones and the role that medication plays in their prevention.
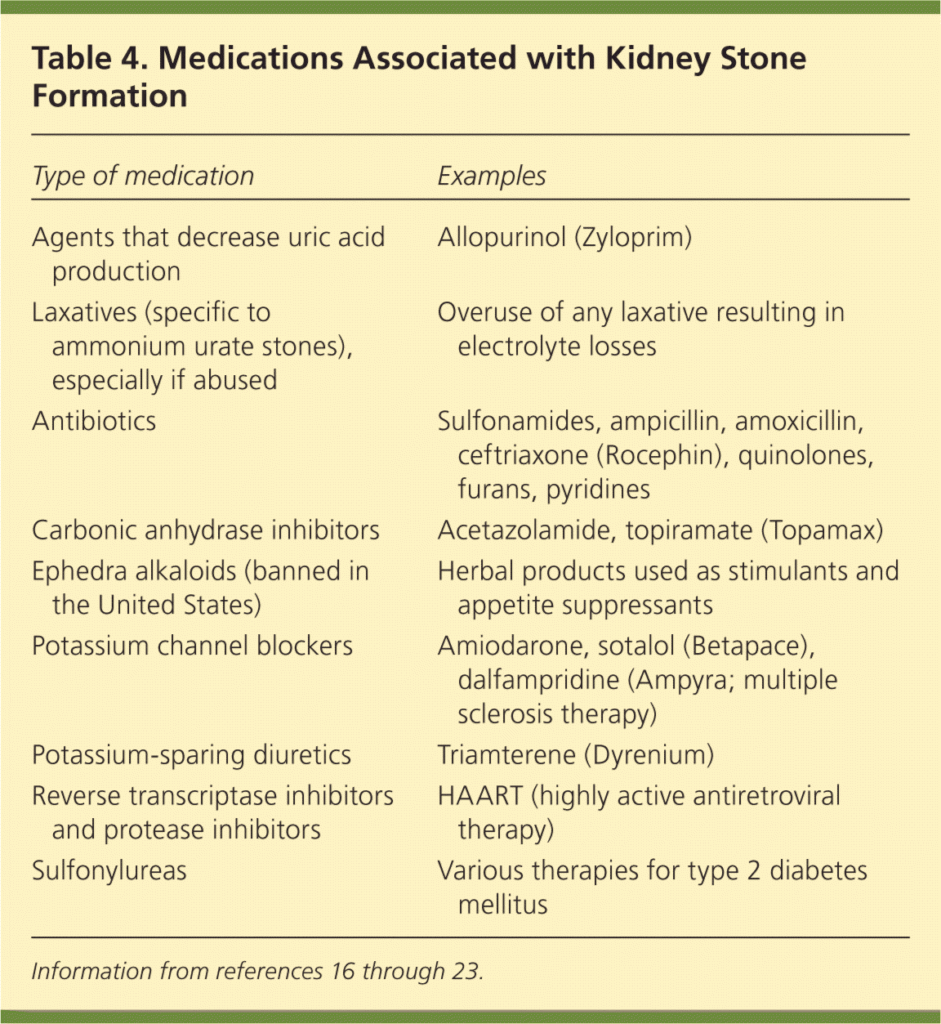
This image is property of www.aafp.org.
Types of Kidney Stones
Before delving into medication management for kidney stones, it is important to understand the different types of kidney stones that can occur. The most common type is the calcium oxalate stone, which occurs when calcium combines with oxalate in the urine. Other types include uric acid stones, struvite stones, and cystine stones. Each type of stone has its own distinct characteristics and may require a slightly different approach to prevention and treatment.
Causes of Kidney Stones
It is essential to be aware of the causes of kidney stones in order to effectively prevent their recurrence. Dehydration is a major factor, as it leads to concentrated urine and an increased likelihood of crystal formation. Certain medical conditions such as hypercalcemia, hyperparathyroidism, and urinary tract infections can also contribute to the formation of kidney stones. Dietary factors, such as a high intake of oxalate-rich foods, sodium, or animal protein, can further increase the risk of stone formation.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
If you experience symptoms such as severe pain in the back or side, blood in your urine, or frequent urination, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds, can be used to visualize the presence and location of kidney stones. Additionally, urine tests may be conducted to analyze the composition of the stones and identify any underlying causes.
Prevention of Kidney Stones
Preventing kidney stones is crucial to avoiding the excruciating pain and potential complications associated with their formation. Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in prevention. Staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water, typically around 8 cups per day, helps to dilute urine and reduce the risk of stone formation. A well-balanced diet that limits sodium, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods can also be beneficial. In certain cases, medication may be prescribed to further reduce the risk of stone recurrence.
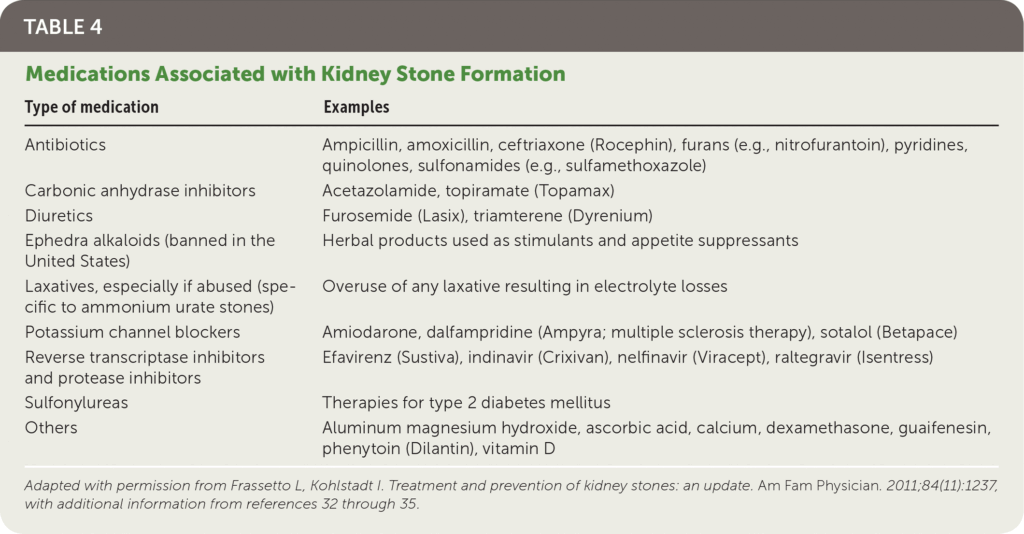
This image is property of www.aafp.org.
Role of Medication in Kidney Stone Prevention
Medication can be a valuable tool in the prevention of kidney stones, especially for individuals with a history of recurrent stones or underlying medical conditions. There are several medications that are commonly used in the management of kidney stone prevention. Let’s explore some of the most commonly prescribed medications and their roles.
1. Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are often prescribed to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. These medications work by increasing the excretion of calcium in the urine, which helps to reduce the concentration of calcium and prevent stone formation. Thiazide diuretics can also decrease the amount of citrate excreted in the urine, which is beneficial in preventing calcium oxalate stones.
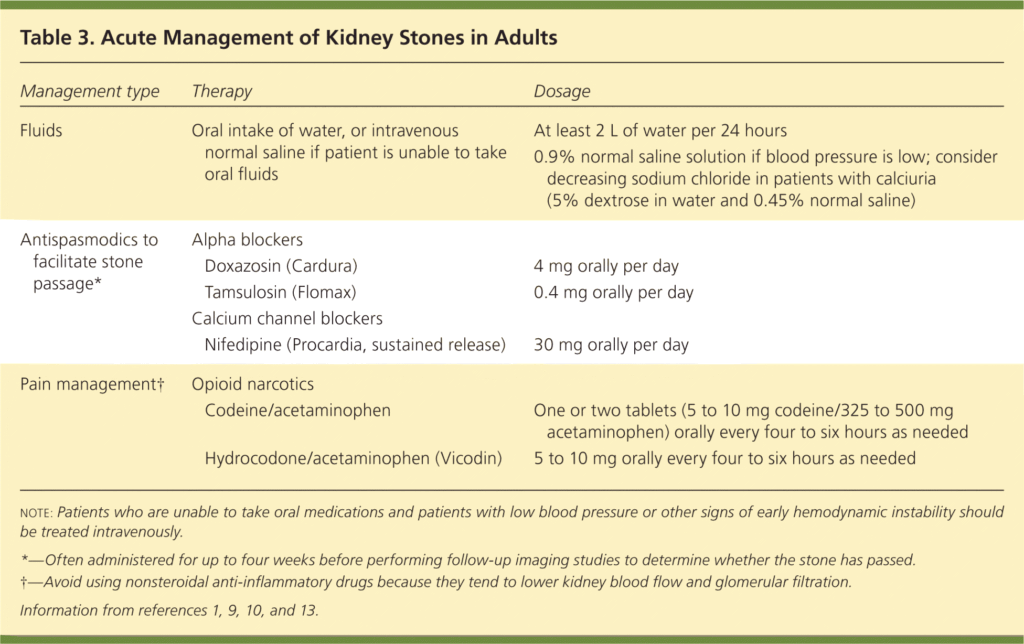
This image is property of www.aafp.org.
2. Allopurinol
Allopurinol is commonly prescribed for individuals who have uric acid stones or high levels of uric acid in their urine. This medication works by inhibiting the production of uric acid in the body, thereby reducing the risk of stone formation. By reducing the levels of uric acid, allopurinol can help dissolve existing uric acid stones and prevent their recurrence.
3. Citrate Supplements
Citrate supplements, such as potassium citrate, are often prescribed to increase the urinary citrate levels. Citrate is a natural inhibitor of stone formation, as it helps to prevent the crystallization of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate. By increasing the citrate levels in the urine, these supplements can reduce the risk of stone formation, particularly in those with low urinary citrate levels.
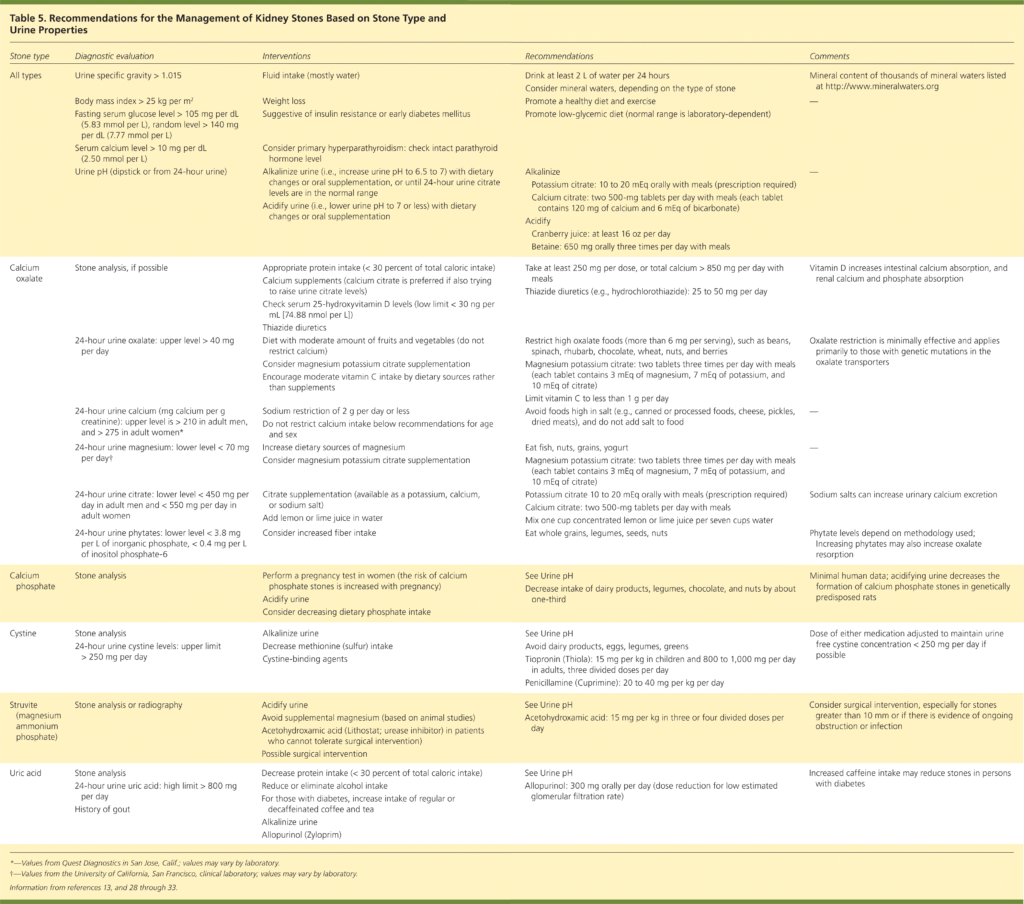
This image is property of www.aafp.org.
4. Antibiotics
In cases where kidney stones are associated with urinary tract infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. These medications are used to treat the infection and reduce the risk of stone formation. By eliminating the bacteria that contribute to stone formation, antibiotics can help prevent recurrent stones and promote overall urinary tract health.
5. Potassium Citrate
Potassium citrate is a medication that is often prescribed to individuals with specific types of kidney stones, such as calcium oxalate or uric acid stones. It helps to increase the urinary pH, making the urine less acidic. This change in pH can prevent the crystallization of certain substances, such as calcium oxalate or uric acid, thereby reducing the risk of stone formation.
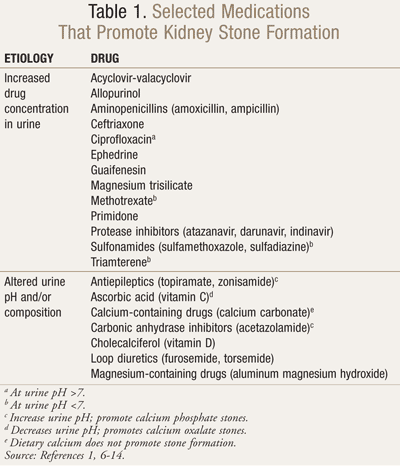
This image is property of www.uspharmacist.com.
6. Phosphate Binders
Phosphate binders, such as calcium acetate or aluminum hydroxide, are commonly used in the management of calcium phosphate stones. These medications work by binding to phosphate in the digestive system, reducing its absorption and decreasing the concentration of phosphate in the urine. By lowering the levels of phosphate, the risk of calcium phosphate stone formation can be significantly reduced.
7. Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers, such as nifedipine, are sometimes prescribed to individuals with certain types of kidney stones, particularly those composed of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate. These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the walls of blood vessels, improving blood flow to the kidneys. By enhancing blood flow and reducing the concentration of calcium in the kidneys, calcium channel blockers can help prevent stone formation.
8. Alpha Blockers
Alpha blockers, such as tamsulosin, are commonly prescribed to individuals with kidney stones that are causing obstruction or difficulty passing through the urinary system. These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the ureter, facilitating the passage of stones and reducing the likelihood of obstruction. Alpha blockers can be particularly beneficial for individuals with larger stones or stones that are causing significant pain.
9. Diuretics as Adjunct Therapy
In some cases, diuretics may be prescribed as adjunct therapy to other medications in order to enhance their effectiveness or reduce side effects. Diuretics increase urine production and can help flush out excess minerals or substances that contribute to stone formation. They are often used in combination with other medications to provide a comprehensive approach to kidney stone prevention.
10. Impact of Medication on Kidney Function
While medications play a crucial role in kidney stone prevention, it is important to consider their potential impact on kidney function. Certain medications, such as thiazide diuretics or potassium citrate, can alter electrolyte levels and may require regular monitoring of kidney function and electrolyte balance. Additionally, it is essential to discuss any existing medical conditions or medications with your healthcare provider to ensure that the prescribed medications for kidney stone prevention do not interact or exacerbate any underlying conditions.
In conclusion, medication management is a valuable and effective approach to kidney stone prevention. By understanding the different types of kidney stones, their causes, and the role medication plays in their prevention, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the likelihood of stone formation and recurrence. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medications and dosages for each individual’s unique situation. Together with lifestyle modifications, medication management can help individuals reduce their risk of kidney stone formation and maintain optimal urinary tract health.

