You may be wondering how to create a well-balanced diet without compromising on managing oxalates. Striking a balance between maintaining a healthy diet and managing the intake of oxalates can seem challenging, but with some guidance and knowledge, it is definitely achievable. In this article, we will explore some effective strategies and tips to help you create a balanced diet while successfully managing oxalates, ensuring that you maintain overall good health without sacrificing your dietary needs.

This image is property of www.kidney.org.
Understanding Oxalates
What are oxalates?
Oxalates are naturally occurring compounds found in many foods. They are a type of antinutrient, meaning that they can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals in the body, such as calcium. Oxalates are present in varying amounts in a wide range of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Sources of oxalates in foods
Some common foods that are high in oxalates include spinach, rhubarb, beets, swiss chard, and chocolate. Other sources include peanuts, almonds, quinoa, and soy products. It’s important to note that the oxalate content can vary depending on the variety, ripeness, and preparation of the food.
The impact of oxalates on health
For most healthy individuals, oxalates from food are not a concern. However, for some people with certain medical conditions, excessive intake of oxalates can lead to the formation of kidney stones. Those who are prone to forming kidney stones may need to limit their consumption of high-oxalate foods in order to manage their condition.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Benefits of a balanced diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients and energy to support bodily functions, promote growth and development, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It helps to ensure that you are getting a wide variety of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients to support optimal health.
Nutritional requirements
A balanced diet should include a variety of foods from all food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is important to meet specific nutritional requirements for macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) as well as micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). The specific requirements may vary depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and underlying health conditions.
Health implications of an imbalanced diet
An imbalanced diet that is lacking in essential nutrients can have negative consequences on your health. It can lead to deficiencies in important vitamins and minerals, which can impair bodily functions and increase the risk of nutrient-related diseases. On the other hand, an excessive intake of certain nutrients, such as saturated fats, added sugars, and sodium, can increase the risk of obesity, heart disease, and other chronic conditions.

This image is property of nourishinghope.com.
Identifying High-Oxalate Foods
Common high-oxalate foods
A variety of plant-based foods contain high levels of oxalates. Some examples of common high-oxalate foods include spinach, beet greens, Swiss chard, rhubarb, and cocoa. Other sources of oxalates include nuts and seeds, such as almonds, peanuts, sesame seeds, and poppy seeds. It’s important to note that while these foods are high in oxalates, they are also rich in other beneficial nutrients.
Hidden sources of oxalates
In addition to the obvious high-oxalate foods, there are also some hidden sources of oxalates that people may not be aware of. For example, certain spices like turmeric and cinnamon can contain moderate levels of oxalates. Some types of tea, such as black tea and green tea, also contain oxalates. By being mindful of these hidden sources, you can better manage your oxalate intake.
Reading food labels for oxalate content
When trying to manage your oxalate intake, reading food labels can be helpful. While oxalate content is not typically listed on nutrition labels, you can look for ingredients that are known to be high in oxalates. For example, if a product contains spinach or almonds, it is likely to have a higher oxalate content. Being mindful of these ingredients can help you make more informed choices about the foods you consume.
Managing Oxalates in the Diet
Working with a healthcare professional
Managing oxalates in the diet can be challenging, especially for individuals with specific health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian, can be beneficial in developing a personalized approach to managing oxalates. They can provide guidance on the appropriate intake of high-oxalate foods and help ensure that your diet remains balanced overall.
Understanding individual tolerance
Everyone’s tolerance to oxalates is different. While some individuals can tolerate higher levels of oxalates without any issues, others may be more susceptible to the formation of kidney stones. It is important to understand your own tolerance and consider any underlying health conditions or medical history that may impact your ability to manage oxalate intake effectively.
Monitoring oxalate intake
Keeping track of your oxalate intake can be helpful in managing your overall diet. You can start by identifying the high-oxalate foods that you frequently consume and making note of their serving sizes. There are also online resources and mobile apps available that provide oxalate content information for various foods. By monitoring your intake, you can make adjustments as needed to ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while keeping oxalate intake within a desired range.

This image is property of khccares.com.
Achieving Balance with Nutrient-Rich Foods
Incorporating high-nutrient, low-oxalate foods
While it may be necessary to limit high-oxalate foods, it is important to ensure that you are still getting a variety of nutrient-rich foods in your diet. Look for low-oxalate options that are high in essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds. Foods such as leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, berries, lean proteins, and whole grains can provide a wide range of nutrients while keeping oxalate levels in check.
Importance of variety in the diet
Eating a variety of foods is key to obtaining a well-rounded nutrient profile and preventing nutrient deficiencies. By diversifying your diet, you can ensure that you are getting a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and other important nutrients necessary for overall health. Including foods from different food groups and trying new recipes or ingredients can help you achieve dietary variety while managing oxalate intake.
Meeting nutritional needs while limiting oxalates
It is possible to meet your nutritional needs while managing your oxalate intake. By focusing on foods that are high in essential nutrients but lower in oxalates, you can strike a balance. For example, if you are limiting high-oxalate greens like spinach, you can opt for other leafy greens such as kale or collard greens that are lower in oxalates but still provide a wealth of nutrients. Planning your meals and snacks to ensure that they include a variety of these nutrient-rich, low-oxalate options can help you maintain a healthy and balanced diet.
Factors Affecting Oxalate Absorption
Cooking methods and oxalate content
The way foods are cooked can impact their oxalate content and potential absorption. Cooking methods such as boiling or steaming can help reduce the oxalate levels in certain foods. On the other hand, roasting or baking foods can increase their oxalate content. Awareness of these cooking methods and their impact on oxalates can assist in managing your oxalate intake effectively.
Food combinations to optimize absorption
Pairing certain foods together can enhance the absorption of oxalates and maximize the nutritional benefits. Combining foods high in oxalates with those that are rich in calcium or vitamin C can help reduce the potential negative effects of oxalates. Calcium can bind to oxalates in the digestive system, preventing their absorption, while vitamin C can help convert oxalates into a form that is less likely to form kidney stones.
Factors affecting oxalate absorption in the gut
Various factors can affect the absorption of oxalates in the gut. These include the health of the gastrointestinal tract, gut bacteria composition, and the presence of other substances that can bind to oxalates. Understanding these factors can provide insight into how oxalates are processed in the body and may help guide dietary choices and lifestyle interventions to manage oxalate absorption effectively.
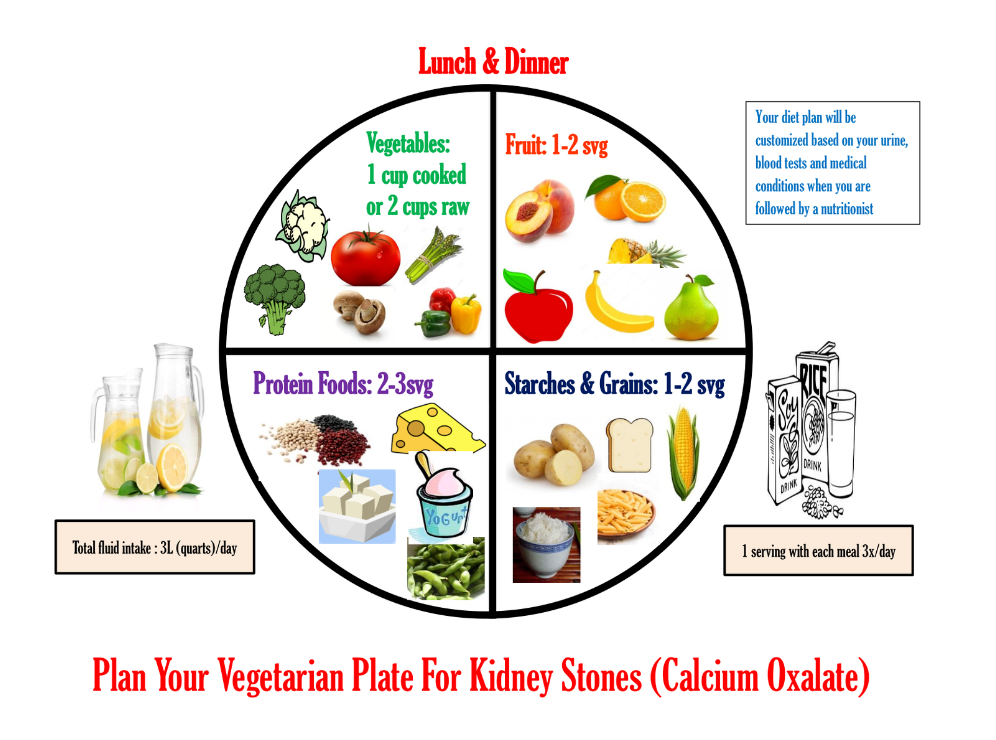
This image is property of www.kidney.org.
Hydration and Oxalate Management
Importance of hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and plays a role in managing oxalate levels. Drinking an adequate amount of fluids helps maintain urine volume and dilution, reducing the risk of oxalate crystallization and stone formation. It is recommended to drink enough water throughout the day to keep urine clear or light yellow in color as an indicator of proper hydration.
Impact of fluid intake on oxalate excretion
Increasing fluid intake can help promote the excretion of oxalates through urine, reducing their concentration in the body. Diluted urine can minimize the risk of oxalate crystallization and the formation of kidney stones. Adequate hydration can also support overall kidney health and optimize urinary function.
Choosing the right beverages
When managing oxalates, it’s important to choose the right beverages to support hydration while considering their oxalate content. Water is the best choice as it is free of oxalates and provides pure hydration. Herbal teas, such as chamomile or peppermint tea, can also be good options. However, it’s important to be cautious with certain beverages that have higher oxalate contents, such as some fruit juices, sodas, and energy drinks.
Supplementation and Oxalate Control
Role of supplements in managing oxalates
In some cases, dietary modifications alone may not be sufficient to effectively manage oxalate intake. In such situations, supplementation may be considered to support oxalate control. Calcium citrate is commonly prescribed as a supplement to bind with oxalates in the gut, reducing their absorption and potential negative effects. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements to ensure their safety and effectiveness for your specific needs.
Consulting with a healthcare professional
Before considering any supplements or making significant changes to your diet, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or urologist. They can assess your individual situation, review your medical history, and provide personalized recommendations to help manage oxalates effectively. They will also consider any potential interactions with medications or existing health conditions in order to develop an appropriate plan.
Understanding potential risks and benefits
It is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits of any supplementation or interventions related to managing oxalates. While calcium citrate can be beneficial in binding with oxalates, excessive calcium supplementation without proper guidance may lead to other health complications. A healthcare professional can help assess the risks and benefits based on your specific needs and provide you with the necessary guidance to make informed decisions.

This image is property of kidneycop.com.
Meal Planning Strategies
Balancing oxalate-rich and oxalate-limited foods
Meal planning plays a vital role in achieving a balanced diet while managing oxalates. It’s important to strike a balance between consuming foods high in oxalates and those that are lower in oxalates. By incorporating a variety of low-oxalate foods, such as leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, you can create well-rounded meals that support overall health while managing your oxalate intake effectively.
Meal prepping for convenience and variety
Meal prepping can be a useful strategy for maintaining a balanced diet while managing oxalates. By preparing meals and snacks in advance, you can ensure that you have a variety of nutritious options readily available. This can help you avoid relying on convenience foods that may be high in oxalates and lacking in essential nutrients. When meal prepping, consider incorporating a mix of ingredients to provide a well-rounded nutrient profile.
Incorporating moderation and portion control
In addition to balancing oxalate-rich and oxalate-limited foods, practicing moderation and portion control is key. It is important to pay attention to portion sizes and be mindful of the frequency of consuming high-oxalate foods. By being aware of your overall oxalate intake and practicing moderation, you can maintain a balanced diet and manage your oxalate levels effectively.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Working with a registered dietitian
When it comes to managing oxalates and creating a balanced diet, seeking guidance from a registered dietitian can be incredibly beneficial. A registered dietitian is a healthcare professional with expertise in nutrition and can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and health goals. They can help develop a customized plan that takes into account your oxalate management requirements while ensuring that you are meeting your nutritional needs.
Customizing a balanced diet plan
A registered dietitian can work with you to create a balanced diet plan that addresses your individual dietary needs, preferences, and goals. They can provide education on oxalate management, help you identify suitable food choices and recipes, and provide ongoing support to help you stay on track. Customizing a balanced diet plan ensures that you are taking a holistic approach to your nutrition while effectively managing your oxalate intake.
Monitoring progress and adjustments
Regular monitoring and review are important when managing oxalates and following a balanced diet. A registered dietitian can help monitor your progress, assess the impact of dietary changes, and make necessary adjustments as needed. They can also provide guidance on tracking your oxalate intake, identifying potential challenges, and offering solutions to overcome them. Regular check-ins with a registered dietitian can help ensure that you are on the right track and achieving your goals effectively.

