Imagine this: you’re expecting a little bundle of joy, and you want to make sure nothing stands in the way of a healthy pregnancy. But have you ever heard of oxalates? These compounds, found in certain foods, have been making waves in the wellness community. Now, you may be wondering, can oxalates affect your pregnancy or prenatal health? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the potential impact of oxalates on expectant mothers and their unborn babies. So, grab a cup of tea, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of oxalates and pregnancy. Pregnancy is a remarkable journey filled with excitement and anticipation. As an expectant mother, you want to ensure the best possible outcome for your baby’s health and development. That’s why it’s important to educate yourself about various factors that can impact pregnancy, including the role of oxalates. In this article, we will explore the definition of oxalates, their potential effects on fertility and the risk of kidney stones. We will also delve into how oxalate intake during pregnancy can influence nutrient absorption, fetal development, and the prevention of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Additionally, we will discuss ways to manage and balance your oxalate intake, the importance of a balanced diet, and the significance of nutrition education and awareness. So, let’s dive in and learn more about the impact of oxalates on pregnancy and prenatal health.
This image is property of www.thekidneydietitian.org.
What are Oxalates?
Oxalates are naturally occurring compounds found in a wide range of foods. They belong to a group of molecules known as organic acids and are derived from oxalic acid. Some commonly consumed foods that contain oxalates include spinach, rhubarb, beets, nuts, seeds, chocolate, and certain types of grains. Oxalates can also be endogenously produced within the body as a byproduct of metabolism. While many parts of the body can handle oxalates effectively, excess amounts can lead to health issues, especially during pregnancy.
Definition of Oxalates
Oxalates, or oxalic acid, are chemical compounds that combine with minerals in the body to form oxalate crystals. These crystals can accumulate in various tissues and organs, potentially leading to the formation of kidney stones and other health complications. Oxalates can also interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients, impacting overall health and wellness.
Sources of Oxalates
As mentioned earlier, oxalates can be found in a variety of foods, both plant-based and animal-derived. Plant-based foods tend to have higher levels of oxalates, with some vegetables, fruits, and nuts being particularly rich sources. On the other hand, animal-based foods, such as meat and dairy products, generally contain lower amounts of oxalates. It’s important to note that cooking or processing foods can affect the oxalate content, with some methods reducing the levels while others may increase them.
Oxalates and Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period of heightened concern for many women, as they strive to ensure a healthy environment for their developing baby. When it comes to oxalates, there are crucial considerations regarding their potential effects on fertility and the risk of kidney stones.
Potential Effect on Fertility
Studies have suggested a possible link between high oxalate consumption and fertility issues. Excess oxalates can bind to calcium, forming calcium-oxalate crystals that may hinder fertilization and implantation. However, further research is needed to establish a definitive connection between oxalates and infertility.
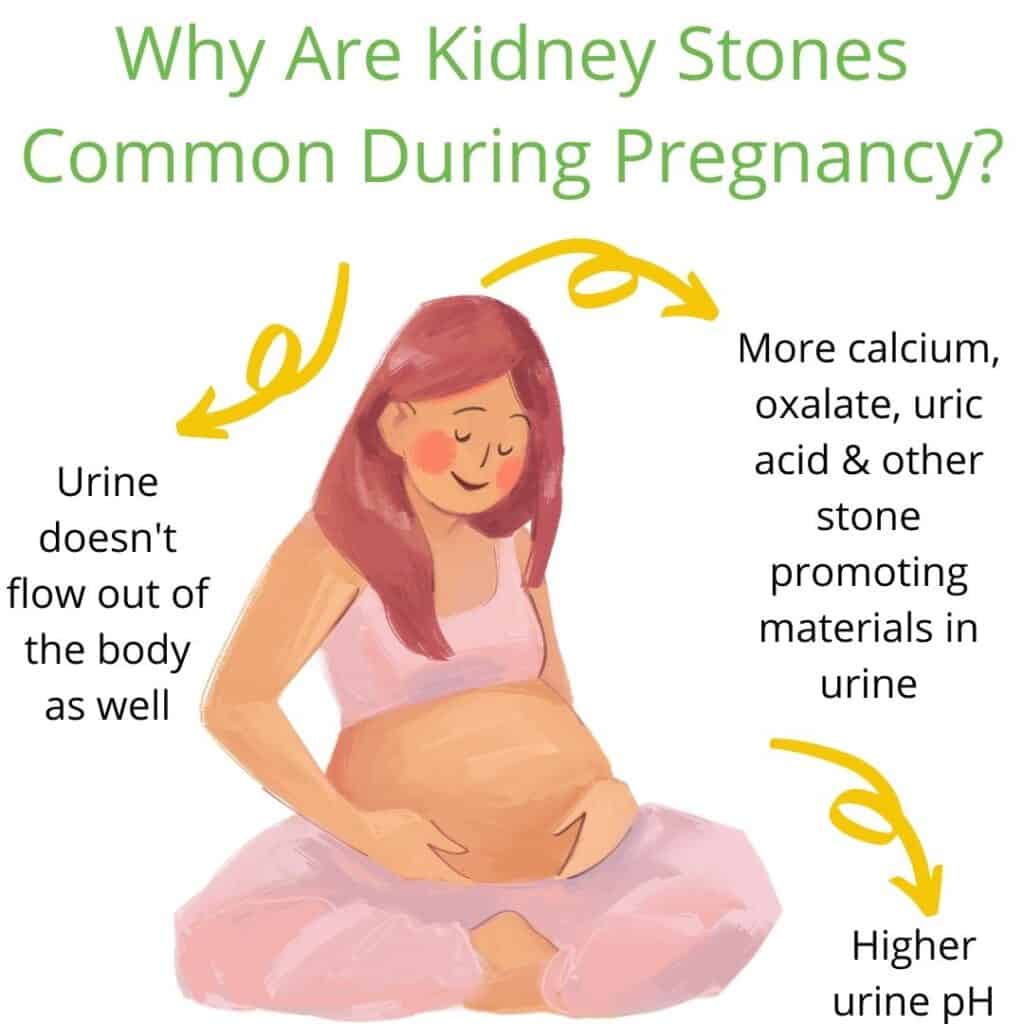
Risk of Kidney Stones
One potential concern during pregnancy is the increased risk of developing kidney stones. Kidney stones can be extremely painful and may require medical intervention. Oxalates contribute to the formation of calcium-oxalate stones when their levels in the urine are high. Therefore, managing oxalate intake is crucial, especially for individuals predisposed to kidney stone formation.

This image is property of kajabi-storefronts-production.kajabi-cdn.com.
Oxalates and Prenatal Health
During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous physiological changes to support the growth and development of the fetus. Oxalate intake can impact both maternal health and prenatal development. Let’s explore how oxalates during pregnancy affect the bioavailability of oxalates, nutrient absorption, and potential impacts on fetal development.
Bioavailability of Oxalates during Pregnancy
Bioavailability refers to the extent to which a nutrient or substance is absorbed and utilized by the body. The bioavailability of oxalates during pregnancy can vary, with some studies suggesting increased absorption rates, potentially due to hormonal changes. This heightened absorption can lead to higher oxalate levels in the body, necessitating caution in managing your oxalate intake.
Influence on Nutrient Absorption
Oxalates can bind to essential minerals in the digestive tract, impairing their absorption into the bloodstream. This can hinder the body’s ability to obtain and utilize vital nutrients. For example, calcium absorption can be negatively affected by high levels of oxalates, which can lead to calcium depletion and pose risks for both the mother and the developing baby.
Potential Impact on Fetal Development
Nutrient deficiencies during pregnancy can have far-reaching consequences for the developing fetus. As oxalates can interfere with nutrient absorption, there is a potential risk of inadequate nutrient delivery to the fetus. This can hinder optimal growth and development and may contribute to a range of health issues, such as low birth weight and developmental disorders. Therefore, managing oxalate intake becomes essential in supporting optimal fetal health.
Managing Oxalate Intake during Pregnancy
Balancing oxalate-rich foods, ensuring adequate calcium intake, and consulting with a healthcare professional are crucial steps in managing your oxalate intake during pregnancy. Let’s explore each of these strategies in more detail.
Balancing Oxalate-Rich Foods
While it may be tempting to completely eliminate oxalate-rich foods from your diet, it’s important to strike a balance. Many of these foods offer valuable nutritional benefits and should not be entirely excluded. Instead, focus on moderating your intake and pairing oxalate-rich foods with calcium-rich choices to help mitigate the potential impact of oxalates.
Importance of Calcium Intake
Calcium plays a vital role in maintaining bone health, supporting muscle function, and facilitating normal nerve transmission. As oxalates can interfere with calcium absorption, ensuring an adequate intake becomes even more crucial during pregnancy. Incorporating calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based alternatives, can help meet your calcium needs.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
Every pregnancy is unique, and it’s essential to work closely with your healthcare professional to tailor your dietary choices and manage any existing health conditions. They can provide personalized guidance on oxalate intake, dietary modifications, and supplementation if necessary. Regular prenatal check-ups will allow for close monitoring of your nutritional status and overall well-being.

This image is property of www.thekidneydietitian.org.
Effects of High Oxalate Consumption during Pregnancy
Consuming high amounts of oxalates during pregnancy can have several adverse effects on maternal and fetal health. Let’s explore the potential increased risk of calcium depletion and inhibition of iron absorption.
Increased Risk of Calcium Depletion
As mentioned earlier, oxalates can bind with calcium, forming crystals that can contribute to the development of kidney stones. This binding process can deplete calcium levels in the body and increase the risk of calcium deficiency. Adequate calcium intake is crucial for supporting bone health, muscle function, and cellular processes, making it essential to manage oxalate consumption to avoid potential calcium depletion.
Potential Inhibition of Iron Absorption
Iron is a vital nutrient during pregnancy, supporting the production of red blood cells and preventing anemia. However, oxalates can interfere with the absorption of non-heme iron, the type of iron present in plant-based foods. This inhibition can impact your body’s ability to efficiently utilize iron, potentially leading to iron-deficiency anemia. Therefore, it’s important to consider both oxalate and iron intake to promote optimal iron absorption and prevent deficiencies.
Incorporating Low-Oxalate Alternatives
To manage your oxalate intake during pregnancy effectively, it can be helpful to incorporate low-oxalate alternatives into your diet. Let’s explore how choosing oxalate-low foods and opting for plant-based calcium sources can be beneficial.
Choosing Oxalate-Low Foods
A well-rounded diet should include a variety of foods, and it’s no different when managing oxalate intake during pregnancy. By actively seeking out low-oxalate alternatives, you can still enjoy a diverse range of tasty meals while reducing your overall oxalate load. Some examples of low-oxalate foods include cucumbers, lettuce, green beans, cauliflower, bananas, and poultry.
Benefits of Plant-Based Calcium Sources
While dairy products are often considered the primary source of calcium, there are numerous plant-based alternatives that can meet your calcium needs. Dark leafy greens, such as kale, broccoli, and collard greens, are excellent calcium sources with lower oxalate content. Fortified plant-based milk, tofu, and sesame seeds are also great options. Incorporating these foods into your diet can provide the necessary calcium while managing oxalate intake.

This image is property of www.momjunction.com.
Oxalate Intake and UTIs during Pregnancy
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common concern during pregnancy and can have serious implications if left untreated. Let’s examine the correlation between oxalate consumption and UTIs and the importance of hydration in preventing infections.
Correlation between Oxalate Consumption and UTIs
Studies have suggested a potential link between high oxalate consumption and an increased risk of UTIs. Excessive oxalate levels in the urine can create a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria that cause UTIs. While more research is needed to establish a definitive association, managing oxalate intake can be a proactive step in reducing the risk of UTIs during pregnancy.
Importance of Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated is essential for overall health and well-being, particularly during pregnancy. Sufficient fluid intake helps to flush out toxins, maintain kidney function, and reduce the concentration of oxalates in the urine. Hydration also supports a healthy urinary system, reducing the risk of UTIs. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day and consult with your healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on your specific needs.
The Significance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial throughout pregnancy, ensuring the intake of adequate nutrients for both maternal health and fetal development. Let’s delve into the importance of obtaining adequate nutrients during pregnancy and the need for varied and nutrient-rich foods.
Obtaining Adequate Nutrients during Pregnancy
Pregnancy places increased demands on the body, necessitating a higher intake of certain nutrients, such as folate, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. A balanced diet that includes a wide variety of foods is key to obtaining these essential nutrients and supporting optimal maternal health and fetal development. By prioritizing nutrient-dense choices, you can enhance the nutritional quality of your diet and better meet the demands of pregnancy.
Importance of Varied and Nutrient-Rich Foods
Variety is the spice of life, and it also plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy. Consuming a range of foods from different food groups ensures a diverse array of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This approach helps to prevent nutrient deficiencies and supports overall health and wellness. Whether it’s colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, or healthy fats, aim for a balanced plate that fuels both you and your growing baby.

This image is property of humanizedhealth.com.
Nutrition Education and Awareness
Promoting knowledge about oxalate intake and encouraging balanced diets in pregnant women are essential steps in ensuring optimal maternal and fetal health. Let’s explore the significance of nutrition education and awareness within the context of oxalates and pregnancy.
Promoting Knowledge about Oxalate Intake
Many women may not be aware of the potential impact of oxalates on pregnancy and prenatal health. By providing accurate information and resources, healthcare professionals can empower pregnant women to make informed decisions about their diets and manage their oxalate intake effectively. This education can help dispel myths and misconceptions surrounding oxalates and promote balanced dietary choices.
Encouraging Balanced Diets in Pregnant Women
Nutrition education and awareness should extend beyond oxalates to encompass the entire spectrum of dietary choices during pregnancy. By emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, healthcare professionals can empower pregnant women to make choices that optimize both their health and the development of their babies.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of oxalates in pregnancy and prenatal health is crucial for expectant mothers. While oxalates can pose potential risks, such as affecting fertility, contributing to kidney stone formation, and interfering with nutrient absorption, managing their intake is achievable. By balancing oxalate-rich foods, ensuring adequate calcium intake, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, you can maintain a healthy and varied diet during pregnancy. Incorporating low-oxalate alternatives and staying hydrated can further support optimal health and reduce the risk of UTIs. Remember, the key is to educate yourself, listen to your body, and make informed choices that promote the well-being of both you and your baby throughout this extraordinary journey.

